This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
proofread
Phosphorus shortage could affect worldwide crop yields

While phosphorus is an essential element for plant metabolism and growth, its future supply under elevated levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide is uncertain. A shortage of this important nutrient could lead to lower crop yields, especially in poorer countries.
"Our research suggests that a reduction in rice yields could be particularly acute in low-income countries under future CO2 scenarios without the input of additional phosphorus fertilizers to compensate, despite the potentially reduced global risk for phosphorus pollution," said Dengjun (Kevin) Wang, an assistant professor of aquatic chemistry in the Auburn University College of Agriculture's School of Fisheries, Aquaculture and Aquatic Sciences.
Wang is one of the co-authors of a paper recently published in the journal Nature Geoscience that examines phosphorus measurements in long-term experiments.
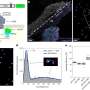
"We looked at measurements of phosphorus concentrations from two long-term (15 and nine years) rice free-air carbon dioxide enrichment, or FACE, experiments," Wang said. "Although no changes were observed in the initial year of the experiments, by the end of the experiments, soil-available phosphorus had declined by more than 20% (26.9% and 21.0% for 15 and nine years, respectively).
"The gathered data were precious and highly convincing since one can rarely find field data in such a big FACE experimentation with decades-long monitoring history in the literature."
The research also suggests that phosphorus reduction can be explained by the production of soil organic phosphorus that is not readily available by plants, as well as by increased removal through crop harvest.
"Our findings further suggest that increased transfers of plant-available phosphorus from biological, biochemical and chemical phosphorus under anthropogenic changes are insufficient to compensate for reductions to plant-available phosphorus under long-term exposure to elevated CO2," Wang said. "This may not be a good sign for us, considering the projected global warming with elevated CO2 level in the atmosphere."
More information: Yu Wang et al, Reduced phosphorus availability in paddy soils under atmospheric CO2 enrichment, Nature Geoscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-022-01105-y
Journal information: Nature Geoscience
Provided by Auburn University at Montgomery