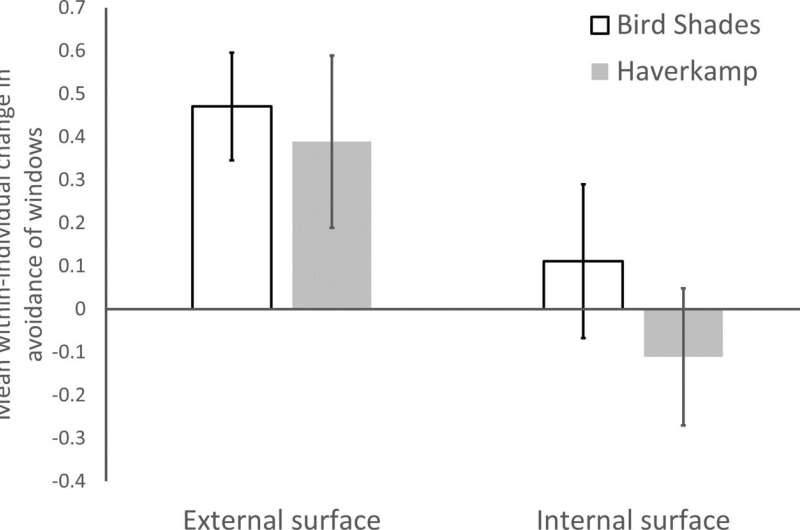
Outcomes of collision avoidance trials. Mean (±SEM) within-individual change in avoidance of collisions with windows. A positive score indicates that birds were more likely to avoid collision when a treatment (BirdShades in white, Haverkamp in gray) was applied to the windows. Credit: PeerJ (2023). DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14676
New research from William & Mary published in PeerJ reveals that decals intended to reduce incidents of bird window strikes—one of the largest human-made causes of bird mortality—are only effective if decals are placed on the outside of the window. Researchers found that the patterns on the films and decals placed on the internal surface of windows do not reduce collision because they may not be sufficiently visible to birds.
Bird window strikes occur when a bird flying near a building cannot perceive a glass windowpane and flies into it. These strikes are a significant concern for bird enthusiasts and conservationists, many of whom advocate for applying visibly noticeable films, patterns, and decals on surfaces of windows to alert birds of the glass.
Many people sympathetic to the potential of bird strikes around their homes or offices tend to apply decals to the inside of their windowpanes, primarily because external application is often logistically difficult and economically prohibitive, especially if the windows are above the first floor of a building. However, the results of this new study show that only external application of these decals can be associated with greater reductions in both window collisions and avian mortality.
Dr. John P. Swaddle, of William & Mary's Institute for Integrative Conservation worked with students Blythe Brewster, Maddie Schuyler, and Anjie Su, to perform the first experimental study to compare the effectiveness of two distinct window films when applied to either the internal or external surface of double-glazed windows. The research team tested two different window film products: BirdShades and Haverkamp. These products were selected for the test because they engage with different wavelenths of light and colors visible to many songbirds.
Using these films, the research team tested the avoidance of window collisions by zebra finches through controlled aviary flight trials. The team employed a design that allowed isolation of the effect of the window treatments on avoidance flight behaviors. A fine mist net in front of the windows prevented actual bird collision during the tests.
The team found consistent evidence that when applied to the external surface of windows, the films resulted in reduced likelihood of collision. However, neither product was effective when the films were applied to the internal surface of windows. Therefore, the results of this research demonstrate the imperative that installers apply these products to exterior surfaces of windows to maximize their protective benefits and reduce the risk of daytime window collision.
"Many people want to reduce bird-window collisions, as these unfortunate events kill hundreds of millions of birds each year," says Dr. Swaddle. "There are lots of decals and window films that will likely make glass surfaces more visible to birds, decreasing collision risk. We were able to show that people must apply decals and films to the external surface of their windows to benefit the birds. We want people to know this as we want their time and money to be well spent—protecting the birds we all love." Swaddle added, "This research was conducted with a team of William & Mary undergraduate researchers, demonstrating the caliber of William & Mary students and the promise of the next generation of conservation researchers."
More information: John P. Swaddle et al, Window films increase avoidance of collisions by birds but only when applied to external compared with internal surfaces of windows, PeerJ (2023). DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14676
Journal information: PeerJ
Provided by PeerJ