This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
written by researcher(s)
proofread
Sex, drugs and alcohol are the top reasons that Texas teachers get in trouble, but overall, such cases are rare
Only about 1 in 200 teachers in Texas are sanctioned for misbehavior, but the largest portion of those sanctions involve sexually related offenses. That's according to a new study we published recently in the Journal of Education Human Resources. The study describes the reasons teachers in Texas are sanctioned for misbehavior, including the frequency and type of violation.
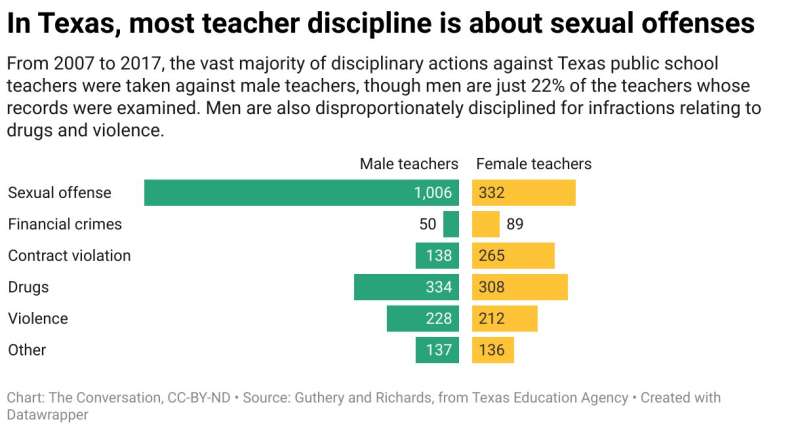
We examined the 3,525 teacher sanctions that took place in Texas from 2007 to 2017. We found that teachers are most frequently sanctioned for sexually related offenses, which accounted for 40% of all reported violations. For sexually related offenses, we include sexual harassment, inappropriate relationships with students and sexual misconduct, whether inside or outside of schools. Examples of sexual misconduct include possession of child pornography or public lewdness.
Drug violations, including possession or sale of controlled substances, providing alcohol to minors or being issued a DUI, accounted for 18.6% of all sanctions, making it the second most common reason for teacher sanctions in Texas.
Contract abandonment accounted for 12.9% of all offenses, making it the third most common offense. Contract abandonment is when a teacher leaves their job before the end of the school year. This is considered an offense against the district.
When a teacher is sanctioned by the State Board for Educator Certification, there is an official record of their discipline case, and punishments can result in a written reprimand on their license, a suspension or permanent revocation of a teaching license. While the overall incidence of sanction is rare, we find patterns of race and gender within who is sanctioned and the types of behavior for which they are sanctioned.
Teachers are frequently in the news for various violations, which can create the impression that teacher misbehavior is widespread. Our study seeks to show just how frequently teachers are in trouble and the nature of those offenses. We also sought to better understand the demographics of teachers who were punished.
While men made up 22% of all of the teachers in our study, they comprise 57.5% of those sanctioned. The greatest gender difference in teacher sanctions is sexual offenses. Male teachers account for 75% of all the sexual offense sanctions. Over the course of our study, 1,006 men were sanctioned for a sexual offense compared with 332 female teachers.
A disproportionate number of Black women were sanctioned for contract abandonment. Specifically, 38 Black women were sanctioned for contract abandonment, accounting for 13.7% of all cases of contract abandonment, while Black women only make up 6.8% of the Texas teacher workforce overall. This finding is significant because historically, due to the school desegregation era and, more recently, as a result of urban public school closures, female teachers of color have disproportionately been forced out of the profession.
In Texas, educators are allowed to resign without penalty during the school year if they can show cause, like moving out of state, having changes to their family's health circumstances, or military reassignment. Teachers are also allowed to resign between school years even if they are on a multiyear contract as long as it is 45 days prior to the start of school.
If the reasons behind teacher discipline is at all similar to those behind student discipline, then research suggests male teachers and teachers of color are most likely being sanctioned more due to bias. It can be challenging to document if male teachers and teachers of color are being sanctioned because they are engaging in more offenses, or if they are more likely to be reported for the offense. This is a question that we believe needs to be explored.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.![]()