Unusual RNA binding properties found in protein essential for germ cell survival
Joining forces with the Ciaudo (IMHS) and Hall (IPW, D-CHAB) labs, the Allain group (IBC) gained structural insights into the unusual mode of RNA recognition by the Dead End protein complemented by biochemical and cellular experiments. The results were published in Nature Communications.
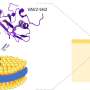
The Dead End (DND1) is essential for the survival of germ cells in vertebrates. The protein has two RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) domains followed by a double-stranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD). Several RNA binding domains are frequently part of the same protein, but the DND1 domain arrangement is only found in two other proteins.
RNA immunoprecipitation experiments showed an essential role of RRM1 in recognizing all tested targets, while the dsRBD only plays a role in binding a subset. The affinity of RRM1 for a single short RNA increased by a factor 80x in the presence of RRM2. The NMR structure revealed the binding consensus sequence and several unusual RNA recognition features by the tandem RRMs: The RNA is sandwiched between the RRMs, and an RRM1 extension is important for binding. Furthermore, a region of RRM2 was found to interact with RNA, which was never previously observed, despite the relatively large number of available RRM-RNA structures.
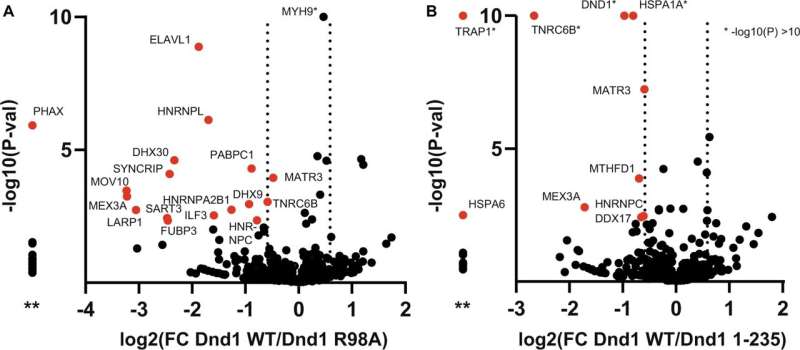
The researchers designed mutants based on the structure to further characterize the DND1 RNA binding properties. In addition, they performed in cellulo experiments, again pointing towards a dispensable role of the dsRBD for RNA recognition while having an important role for the in vivo function likely independent of RNA binding. Finally, DND1 interactome analysis by Mass Spec led the researchers to discuss the possibility that DND1 could be part of granular structures.
More information: Malgorzata M. Duszczyk et al, The solution structure of Dead End bound to AU-rich RNA reveals an unusual mode of tandem RRM-RNA recognition required for mRNA regulation, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-33552-x
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by ETH Zurich