New hybrid electrolyte for high performance Li-ion batteries
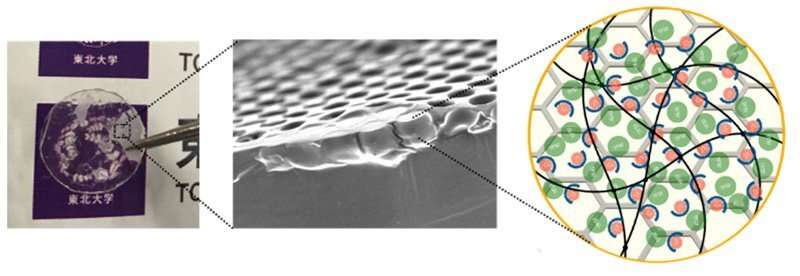
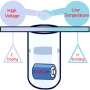
Li-ion batteries (LIBs) are widely used batteries that support modern ITC society, including smartphones and EVs. LIBs are repeatedly charged and discharged by Li-ions passing back and forth between the positive and negative electrodes, with the Li-ion electrolyte acting as a passageway for the ions.
Normally, organic electrolytes such as liquid ethylene carbonate (EC) and their gels have been used as the Li-ion electrolyte due to their voltage resistance and ionic conductivity. However, as liquids and gels are flammable, a switch to safer polymeric solid electrolytes is preferable.
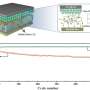
Polymeric solid electrolytes such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) have been proposed as impact-resistant Li-ion electrolytes. However, PEG-based polymer electrolytes crystallize near room temperature, resulting in a significant drop in Li-ion conductivity to around 10-6 S/cm at room temperature.
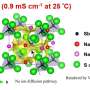
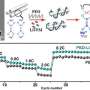
To solve this problem, a research group has invented a new type of polymeric solid electrolyte by combining a porous polymer membrane with several micron pores and a photo-cross-linkable polyethylene glycol PEG-based polymer electrolyte. The polymeric solid electrolyte realized a wide potential window (4.7 V), a high Li-ion conductivity in the 10-4 S/cm class, which is equivalent to a liquid and sufficient for practical use, and a high Li-ion transference number (0.39).
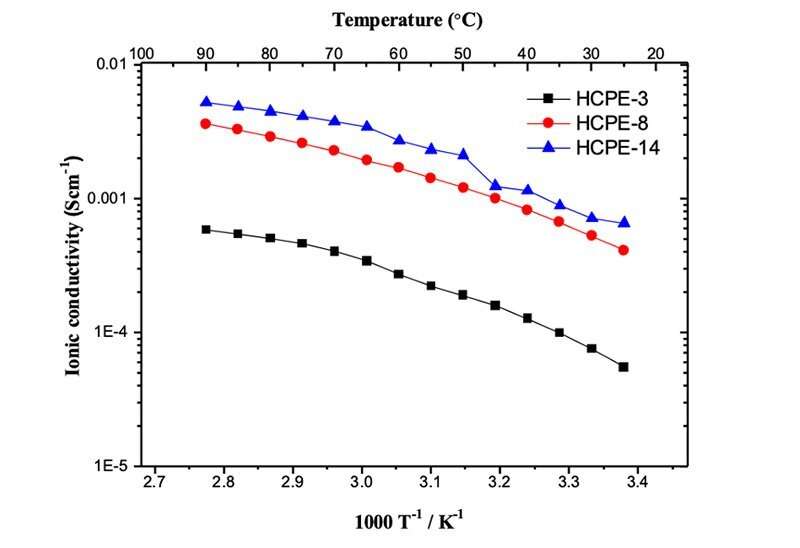
Li-ions transferring in the electrolyte move in various directions due to natural diffusion. The distance is several µm to 10 µm and does not always move linearly between electrodes, which is one of the reasons for the decrease in ionic conductivity. In the present study, therefore, the performance of photo-cross-linked PEG-based solid polymer electrolytes was improved by compositing them with micron-sized porous membranes.
This polymeric solid electrolyte not only shows high performance as an electrolyte but is also expected to be effective in deterring the formation of Li dendrites (dendritic crystals), which can cause ignition, due to the inclusion of a porous membrane. Through the realization of safe, high-performance LIBs, this achievement will contribute to the realization of a sustainable energy supply, which is the seventh goal of the SDGs.
The study is published in iScience.
More information: Manjit Singh Grewal et al, Increasing the ionic conductivity and lithium-ion transport of photo-cross-linked polymer with hexagonal arranged porous film hybrids, iScience (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104910
Journal information: iScience
Provided by Tohoku University