Astronomers obtain new images of R136, the most massive star ever found
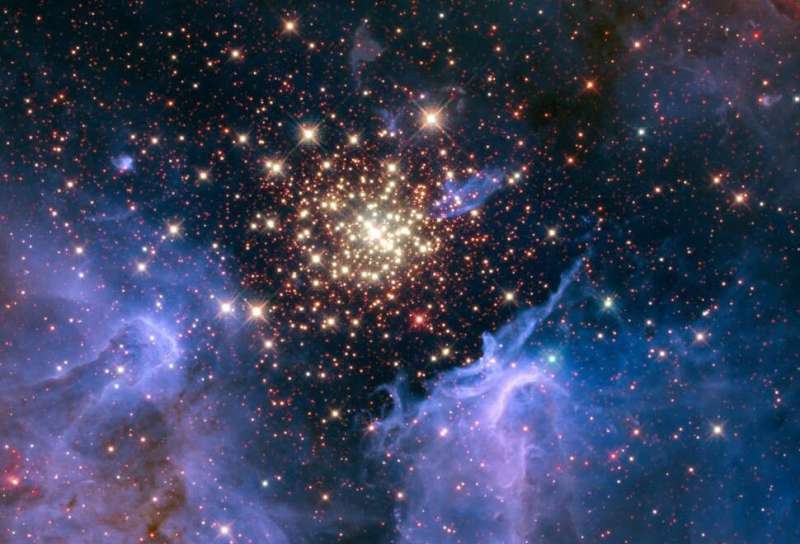

Meet R136a1, the most massive star known. Located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, it's a hulking behemoth weighing somewhere between 150 and 200 times the mass of the sun. Understanding the upper limit of stars helps astronomers piece together everything from the life cycles of stars to the histories of galaxies.
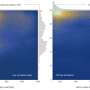
A team of astronomers has studied in detail the star cluster known as R136. This star cluster is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud about 150,000 light-years from Earth. The star cluster itself is huge, featuring many incredibly bright newborn stars.
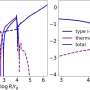
Based on the image, the astronomers were able to estimate the masses of some of the stars, including R136a1, which they estimate has a mass somewhere between 150 and 200 times the mass of the sun. This latest estimate is significantly lower than previous estimates of this same star. Despite that new estimate, however, R136a1 still has a surface temperature eight times hotter than the sun and a radius forty times bigger.
It's likely that R136a1 represents one of the most massive stars in the universe. Stars form in a variety of sizes, from red dwarfs a tenth the mass of the sun to these giants that would put our home star to shame. Understanding how common supergiant stars are helps astronomers understand their formation mechanisms. After all, you need a lot of gas collapsing in a very brief amount of time in order to form a giant star like this. And since there are so massive, they do not live long, so they are that much more difficult to detect.
Galaxies live their lives constantly turning out generation after generation of stars. The ability to make large stars depends on the existence of previous generations. This is because when stars die they release their fused heavy elements out into the interstellar medium. Those heavy elements help other clouds of gas cool quickly to collapse and form bigger stars without fragmenting into many smaller ones.
The more we learn about giant stars like R136a1, the more we learn about the history of galaxies
More information: Resolving the core of R136 in the optical, arXiv:2207.13078v2 [astro-ph.SR]. doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2207.13078
Provided by Universe Today