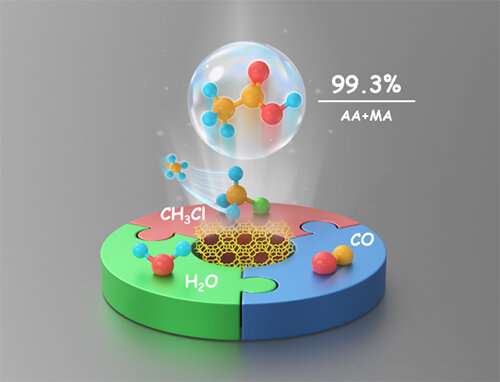
Direct transformation of CH3Cl to acetic acid through a carbonylation reaction
Methane, the main component of natural gas, shale gas and flammable ice, is a clean and inexpensive chemical feedstock with abundant reserves. Nevertheless, the high C-H band energy and low polarizability of a methane molecule inhibit the utilization of methane.
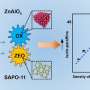
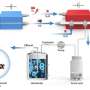
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Liu Zhongmin and Prof. Zhu Wenliang from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed a novel route to directly transform CH3Cl to acetic acid through a carbonylation reaction using acidic zeolites as the catalyst.
The study was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on May 30.
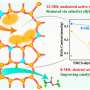
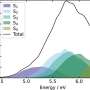
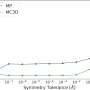
The researchers used pyridine-treated MOR as catalysts to achieve high acetic acid and methyl acetate selectivity. They found that the coupling of CH3Cl with CO and H2O occurred over acidic zeolites especially one-dimensional with 8-member ring (8 MR) or 10-member ring (10 MR).
In particular, the selectivity of acetic acid and methyl acetate reached 99.3% over pyridine-treated MOR under the optimized conditions, which was superior to that of Rh/AC under CH3I-free conditions. The Bronsted acid sites in 8 MR were proven to be the main active site for chloromethane carbonylation.
Moreover, with multiple characterizations, the researchers proposed the reaction mechanism which included the chemical adsorption of CH3Cl, the formation of acetyl groups, and the hydrolysis of acetyl groups.
"Our study may present potential in the efficient and practical transformation of methane into oxygenates in the future," said Prof. Zhu.
More information: Xudong Fang et al, Highly Selective Carbonylation of CH3Cl to Acetic Acid Catalyzed by Pyridine‐Treated MOR Zeolite, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2022). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202203859
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences