New imaging method makes tiny robots visible in the body
Microrobots have the potential to revolutionize medicine. Researchers at the Max Planck ETH Centre for Learning Systems have now developed an imaging technique that for the first time recognizes cell-sized microrobots individually and at high resolution in a living organism.
How can a blood clot be removed from the brain without any major surgical intervention? How can a drug be delivered precisely into a diseased organ that is difficult to reach? Those are just two examples of the countless innovations envisioned by the researchers in the field of medical microrobotics. Tiny robots promise to fundamentally change future medical treatments: one day, they could move through patient's vasculature to eliminate malignancies, fight infections or provide precise diagnostic information entirely noninvasively. In principle, so the researchers argue, the circulatory system might serve as an ideal delivery route for the microrobots, since it reaches all organs and tissues in the body.
For such microrobots to be able to perform the intended medical interventions safely and reliably, they must not be larger than a biological cell. In humans, a cell has an average diameter of 25 micrometers—a micrometer is one millionth of a meter. The smallest blood vessels in humans, the capillaries, are even thinner: their average diameter is only 8 micrometers. The microrobots must be correspondingly small if they are to pass through the smallest blood vessels unhindered. However, such a small size also makes them invisible to the naked eye—and science too, has not yet found a technical solution to detect and track the micron-sized robots individually as they circulate in the body.
Tracking circulating microrobots for the first time
"Before this future scenario becomes reality and microrobots are actually used in humans, the precise visualization and tracking of these tiny machines is absolutely necessary," says Paul Wrede, who is a doctoral fellow at the Max Planck ETH Center for Learnings Systems (CLS).
"Without imaging, microrobotics is essentially blind," adds Daniel Razansky, Professor of Biomedical Imaging at ETH Zurich and the University of Zurich and a member of the CLS. "Real-time, high-resolution imaging is thus essential for detecting and controlling cell-sized microrobots in a living organism." Further, imaging is also a prerequisite for monitoring therapeutic interventions performed by the robots and verifying that they have carried out their task as intended. "The lack of ability to provide real-time feedback on the microrobots was therefore a major obstacle on the way to clinical application."
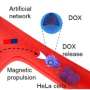
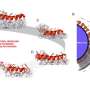
Together with Metin Sitti, a world-leading microrobotics expert who is also a CLS member as Director at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (MPI-IS) and ETH Professor of Physical Intelligence, and other researchers, the team has now achieved an important breakthrough in efficiently merging microrobotics and imaging. In a study just published in the scientific journal Science Advances, they managed for the first time to clearly detect and track tiny robots as small as five micrometers in real time in the brain vessels of mice using a non-invasive imaging technique.
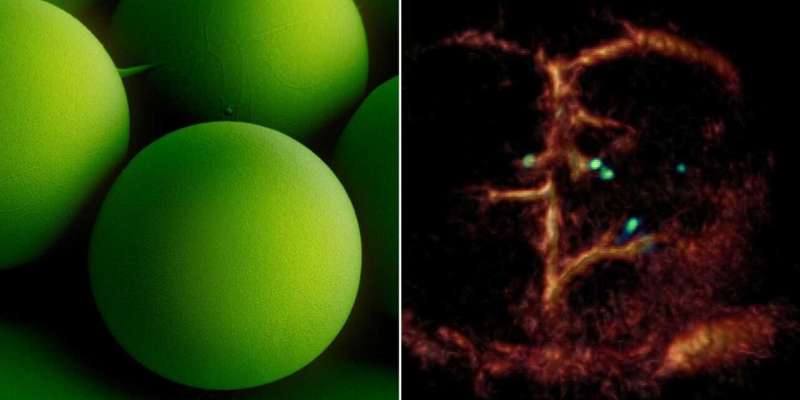
The researchers used microrobots with sizes ranging from 5 to 20 micrometers. The tiniest robots are about the size of red blood cells, which are 7 to 8 micrometers in diameter. This size makes it possible for the intravenously injected microrobots to travel even through the thinnest microcapillaries in the mouse brain.
The researchers also developed a dedicated optoacoustic tomography technology in order to actually detect the tiny robots one by one, in high resolution and in real time. This unique imaging method makes it possible to detect the tiny robots in deep and hard-to-reach regions of the body and brain, which would not have been possible with optical microscopy or any other imaging technique. The method is called optoacoustic because light is first emitted and absorbed by the respective tissue. The absorption then produces tiny ultrasound waves that can be detected and analyzed to result in high-resolution volumetric images.
Janus-faced robots with gold layer
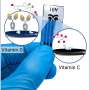
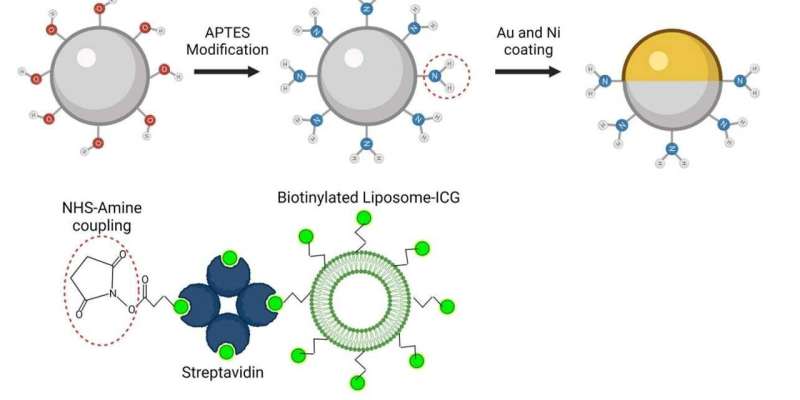
To make the microrobots highly visible in the images, the researchers needed a suitable contrast material. For their study, they therefore used spherical, silica particle-based microrobots with a so-called Janus-type coating. This type of robot has a very robust design and is very well qualified for complex medical tasks. It is named after the Roman god Janus, who had two faces. In the robots, the two halves of the sphere are coated differently. In the current study, the researchers coated one half of the robot with nickel and the other half with gold.
"Gold is a very good contrast agent for optoacoustic imaging," explains Razansky, "without the golden layer, the signal generated by the microrobots is just too weak to be detected." In addition to gold, the researchers also tested the use of small bubbles called nanoliposomes, which contained a fluorescent green dye that also served as a contrast agent. "Liposomes also have the advantage that you can load them with potent drugs, which is important for future approaches to targeted drug delivery," says Wrede, the first author of the study. The potential uses of liposomes will be investigated in a follow-up study.
Furthermore, the gold also allows to minimize the cytotoxic effect of the nickel coating—after all, if in the future microrobots are to operate in living animals or humans, they must be made biocompatible and non-toxic, which is part of an ongoing research. In the present study, the researchers used nickel as a magnetic drive medium and a simple permanent magnet to pull the robots. In follow-up studies, they want to test the optoacoustic imaging with more complex manipulations using rotating magnetic fields.
"This would give us the ability to precisely control and move the microrobots even in strongly flowing blood," says Metin Sitti. "In the present study we focused on visualizing the microrobots. The project was tremendously successful thanks to the excellent collaborative environment at the CLS that allowed combining the expertise of the two research groups at MPI-IS in Stuttgart for the robotic part and ETH Zurich for the imaging part," Sitti concludes.
More information: Paul Wrede et al, Real-time 3D optoacoustic tracking of cell-sized magnetic microrobots circulating in the mouse brain vasculature, Science Advances (2022). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm9132
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by ETH Zurich