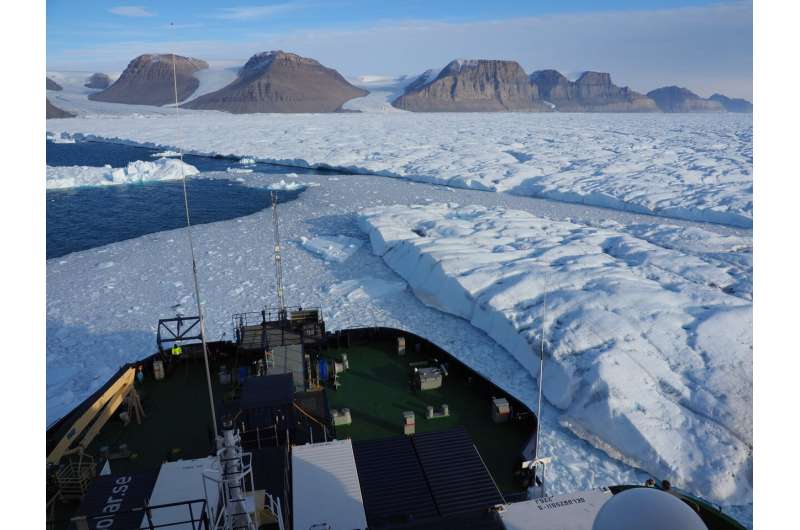
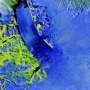
Swedish icebreaker Oden at the front of Petermann Ice Shelf in 2019. The new study shows that if the ice shelf breaks up, it will be difficult to rebuild it. Credit: Martin Jakobsson
Ice shelves are floating extensions of glaciers. If Greenland's second largest ice shelf breaks up, it may not recover unless Earth's future climate cools considerably. This is the result of a new study, published in Nature Communications.
A team of scientists from Stockholm University and University of California Irvine investigated whether the Petermann Ice Shelf in northern Greenland could recover from a future breakup due to climate change. They used a sophisticated computer model to simulate the potential recovery of the ice shelf.
"Even if Earth's climate stopped warming, it would be difficult to rebuild this ice shelf once it has fallen apart," says Henning Åkesson, who led the study at Stockholm University.
"If Petermann's ice shelf is lost, we would have to go 'back in time' towards a cooler climate reminiscent of the period before the industrial revolution to regrow Petermann," Åkesson says.
Ice shelves reduce mass loss from our polar ice sheets. These gatekeepers thereby limit sea-level rise caused by climate warming. "The rationale to avoid breakup of ice shelves in the first place should be clearer than ever," Åkesson says.
Glaciers are rapidly melting
Petermann is one of Greenland's few remaining ice shelves, and is being watched by Argus-eyed scientists worldwide after Manhattan-sized icebergs broke off from the ice shelf in 2010 and 2012, causing Petermann to lose 40 percent of its floating ice shelf. Scientist are concerned that further breakup or even collapse of the ice shelf would speed up ice flow from the interior ice sheet. In 2018, a new crack in the middle of the ice shelf was discovered, which renewed worries of Petermann's state of health.
Ice-sheet experts are concerned
While this study focused on northwestern Greenland's largest glacier, another grave concern is that the larger ice shelves found in Antarctica could be difficult to build back as well, should they break-up too.
"This is just the first step, but chances are that our findings are not unique for Petermann Glacier and Greenland," Åkesson says. "If they are not, near-future warming of the polar oceans may push the ice shelves protecting Earth's ice sheets into a new retreated high-discharge state which may be exceedingly difficult to recover from."
The ice-sheet experts stress that we need to pin down exactly how ice shelves break-up, and how much more warming they now can withstand before they fall apart.
More information: Henning Åkesson et al, Petermann ice shelf may not recover after a future breakup, Nature Communications (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29529-5
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Stockholm University