April 7, 2022 report
Two new Saturn-mass exoplanets discovered
An international team of astronomers reports the detection of two new Saturn-mass exoplanets as part of the CARMENES radial velocity survey. The newly found alien worlds, designated TYC 2187-512-1 b and TZ Ari b, orbit nearby M-dwarf stars. The finding was presented in a paper published March 30 on arXiv.org.
Thanks to the radial velocity (RV) technique, more than 600 exoplanets have been detected so far and more than 100 of them have been found around M dwarfs. The Calar Alto high-Resolution search for M dwarfs with Exoearths with Near-infrared and optical Echelle Spectrographs (CARMENES) project has been crucial in the search for new alien worlds orbiting these most common stars in our galaxy.
Recently, a group of researchers led by Andreas Quirrenbach of Heidelberg University in Germany has announced the discovery of another two extrasolar worlds as part of the CARMENES survey. The observations conducted with the 3.5 m telescope at the Calar Alto observatory in Almería, Spain, have confirmed that two nearby M dwarfs, TYC 2187-512-1 and TZ Ari, host massive planets.
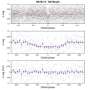
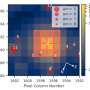
"Here, we report on the discovery of two Saturn-mass planets from the CARMENES survey, which is currently carrying out precise radial-velocity observations of a sample of 387 M dwarfs," the astronomers wrote in the paper.
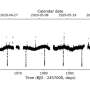
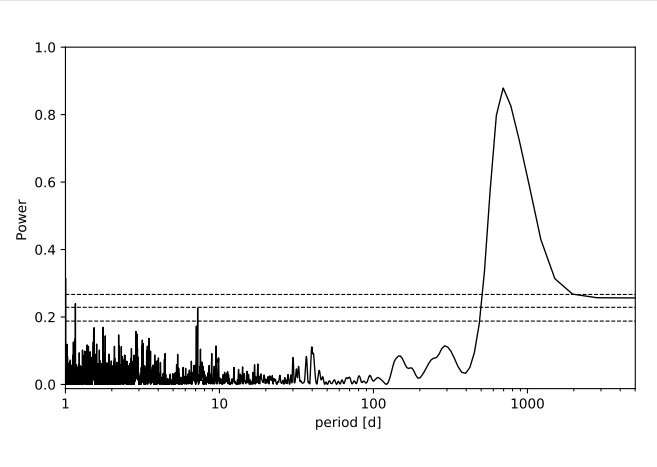
At a distance of some 50.46 light years, TYC 2187-512-1 b orbits its host every 692 days on a near-circular orbit, at a distance of about 1.22 AU from the star. The planet's minimum mass was estimated to be 0.33 Jupiter masses. The parent star TYC 2187-512-1 is of spectral type M1.0 V and is about half the size and mass of our sun. Its effective temperature was measured to be 3,734 K.
TZ Ari b has a mass of at least 0.21 Jupiter masses. The orbital period of this planet was measured to be 771 days, while its orbital eccentricity is at a level of 0.46. The results indicate that the exoplanet is separated by approximately 0.88 AU from TZ Ari. The host star turns out to have spectral type M5.0 V and effective temperature of 3,154 K. This M dwarf is more than six times smaller and less massive than the sun. The system is located about 14.57 light years away.
The authors of the paper underlined that the parameters of TZ Ari b make it a unique planet among other known giant exoworlds. They noted that it is only the second confirmed giant planet orbiting a star with a mass below 0.3 solar masses.
"In fact, the mass of TZ Ari is only 0.15 solar masses, similar to that of GJ 3512, the other low-mass host of a gas giant planet. These two systems occupy an extreme region of the planet mass / host mass parameter space, where disk fragmentation appears to be a more likely formation mechanism than build-up of a core through planetesimal or pebble accretion," the researchers explained.
In concluding remarks, the astronomers revealed that according to their calculations, an occurrence rate of giant planets orbiting M dwarfs with periods up to two years should be within the range between 2 to 6%. They noted that the completion of the CARMENES survey would put more constraints on this number.
More information: A. Quirrenbach et al, The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs: Two Saturn-mass planets orbiting active stars. arXiv:2203.16504v1 [astro-ph.EP], arxiv.org/abs/2203.16504
Provided by Science X Network
© 2022 Science X Network