Breaking down plastic into its constituent parts
A team of ETH researchers led by Athina Anastasaki have succeeded in breaking down plastic into its molecular building blocks and in recovering over 90% of them. A first step towards genuine plastic recycling.
The chemical industry has a long tradition of producing polymers. This involves turning small molecular building blocks into long chains of molecules that bond together. Polymers are the basis of all kinds of everyday plastics, such as PET and polyurethane.
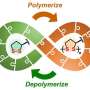
However, while the formation of polymers is well established and well researched, scientists have given little attention to how polymer chains are broken down (a process called depolymerization) to recover their individual building blocks—monomers. One reason for this is that breaking down polymers is a complex process. Whether a polymer can be broken back down at all into its constituent parts depends on which of the different polymer manufacturing processes were used. Another reason is that the depolymerization processes used to date require a lot of energy, which has made them economically unviable. Added to this is the fact that recycled polymers are usually only used in the manufacture of low-value products.
Breaking down polymers is the goal
Athina Anastasaki, Professor of Polymeric Materials at ETH Zurich, wants to change this. She has set herself the goal of producing polymers that can be easily broken down into their building blocks so that they can be fully recycled.
The materials scientist has been able to take a first important step in this direction: A study by her group has just been published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society. In it, Anastasaki and her colleagues show that they can break down certain polymers into their basic building blocks—monomers—and recycle them for use in materials for further applications.
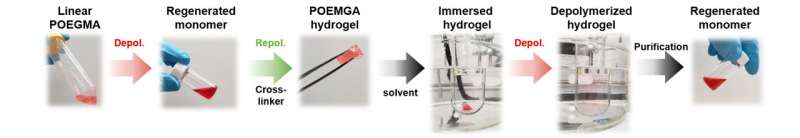
The polymers broken down are polymethacrylates (e.g. Plexi Glass) that were produced using a specific polymerization technique called reversible addition-fragmentation chain-transfer polymerization—otherwise known as RAFT. This relatively new method, which is now also attracting the interest of industry, produces polymer chains of uniform length.
First success
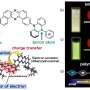
The researchers at ETH Zurich have succeeded in recovering up to 92% of the building blocks of polymethacrylates without adding a catalyst that would enable or accelerate the reaction. "Our method could conceivably be developed even further to involve the use of a catalyst. This could increase the amount recovered even more," says Anastasaki.
The chemical group present at the end of a polymer chain is crucial for the polymer's breakdown. By heating the polymer solvent mixture to 120°C, the researchers created what are referred to as "radicals" at the end of a polymethacrylate chain, which triggered the depolymerization. Researchers at the Australian National University in Canberra were able to confirm the results mathematically.
Producing the same or a different product
According to Anastasaki, the building blocks recovered in this way can be used to produce the same polymer or a completely different product—an insoluble hydrogel that can also be broken down into its monomers. The newly created products are of similar quality to the original ones. This is in contrast to previous products made from recycled polymers.
But there is a catch: "Products made with RAFT polymerization are more expensive than conventional polymers," says Anastasaki. To address this drawback, she and her group are already working on expanding the method for large-scale applications, which will make it more competitive and the resulting products cheaper. The researchers also aim to increase the amount retrieved and recover all the building blocks of a polymer.
The materials scientist is also researching whether other polymers can be depolymerized. She is particularly interested in polystyrene, a widespread, low-cost plastic that is used in many areas of everyday life (Styrofoam).
Method will not resolve the plastics problem short term
Even if this new method raises hopes of solving mankind's plastic waste problem, Anastasaki dismisses the idea for the time being. There is no quick fix to the problem. She goes on to say. "It will take a lot of time and research before the process is established in the chemical industry." Nor will it get rid of plastic waste: today's polymers cannot be broken down in this way. Some new, suitable polymers have to come into circulation before their building blocks can be recovered. But the method has one advantage: no new chemical plants are needed for its introduction and use.
"We are only at the beginning of our research into depolymerization. There are over 30,000 studies on developing new polymerization strategies, with only a handful of them addressing the subject of monomer recovery," says Anastasaki.
More information: Hyun Suk Wang et al, Reversing RAFT Polymerization: Near-Quantitative Monomer Generation Via a Catalyst-Free Depolymerization Approach, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2022). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c00963
Journal information: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Provided by ETH Zurich