High-power laser being constructed for a new experimental facility

Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's decades of leadership in developing high-energy lasers is being tapped to provide a key component of a major upgrade to SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory's Linac Coherent Light Source (LCLS).
Over the next several years, LLNL's Advanced Photon Technologies (APT) program will design and construct one of the world's most powerful petawatt (quadrillion-watt) laser systems for installation in an upgraded Matter in Extreme Conditions (MEC) experimental facility at LCLS, funded by the Department of Energy's Office of Science-Fusion Energy Sciences program.
The new laser will pair with the LCLS X-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) to advance the understanding of high-energy density (HED) physics, plasma physics, fusion energy, laser-plasma interactions, astrophysics, planetary science and other physical phenomena.
The existing MEC facility uses optical lasers coupled to X-ray laser pulses from LCLS to probe the characteristics of matter at extreme temperatures and pressures. MEC experiments have produced groundbreaking science, such as the first observations of "diamond rain" under conditions thought to exist deep inside giant icy planets like Uranus and Neptune.
The MEC-Upgrade (MEC-U) is motivated in part by increasing calls for the United States to re-establish world-class leadership in high-power laser technology, such as in the 2018 National Academies of Science, Engineering, and Medicine report, "Opportunities in Intense Ultrafast Lasers: Reaching for The Brightest Light."
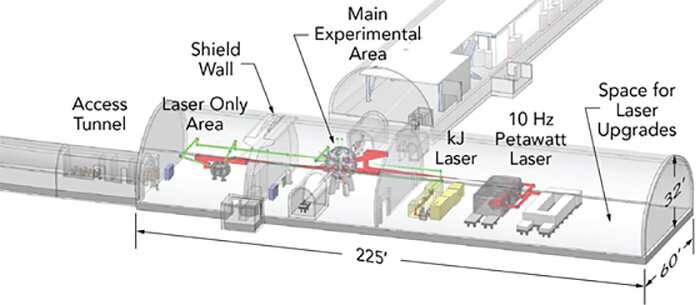
SLAC is partnering with LLNL and the University of Rochester's Laboratory for Laser Energetics (LLE) to design and construct the MEC-U facility in a new underground cavern. LLNL's rep-rated laser (RRL), able to fire at up to 10 Hz (10 pulses per second), and a high-energy kilojoule laser developed by LLE will feed into two new experimental areas containing a target chamber and a suite of dedicated diagnostics tailored for HED science.
The LCLS, part of SLAC's two-mile-long linear particle accelerator in Menlo Park, Calif., is capable of delivering 120 X-ray pulses a second, each one lasting a few femtoseconds (quadrillionths of a second). A concurrent upgrade dubbed LCLS-II will deliver a million pulses a second in an almost continuous X-ray beam that, on average, will be 10,000 times brighter and will double the X-ray energy previously attainable.
"The new high-power lasers being designed by Livermore and Rochester are world-leading in their own right," said Alan Fry, the MEC-U project director. "Coupling them to LCLS dramatically increases their scientific utility and the combination will be an unprecedented capability."
"With the 10-Hz petawatt laser that we're building, along with LLE's long-pulse compression laser and the upgraded LCLS capabilities, the LCLS and its MEC-U facility will become the U.S. flagship for high-repetition-rate, laser-driven HED experiments," said Vincent Tang, NIF & Photon Science program director for High Energy Density and Photon Systems.
"Marrying the latest and the best ultrafast laser technologies with the LCLS beamline at the MEC-U facility will give the United States a fundamentally new high-throughput HED capability for discovery science and national security research," Tang added. "We will be able to rapidly increase our understanding of plasmas and materials at extreme pressures and temperatures, while advancing our ability to operate HED technologies and systems at a repetition rate and scale relevant to important future applications like inertial fusion energy."
The National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) has expressed interest in partnering with the Office of Science to augment the upgrade with additional high-energy long-pulse laser capabilities to further support NNSA's science-based Stockpile Stewardship Program. Among the goals would be to improve scientists' ability to predict the performance of next-generation, stewardship-relevant materials in extreme environments; study the microphysics of inertial confinement fusion; and enable the study of larger volumes of high-atomic-number materials than previously possible.
HAPLS supercharged
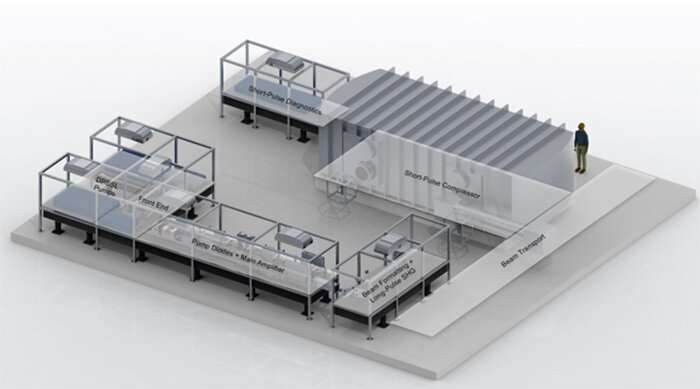
Tom Spinka, project manager and chief scientist for LLNL's RRL, said that it will be a simplified and more energetic version of the High-Repetition-Rate Advanced Petawatt Laser System (HAPLS), designed and developed by the APT Program from 2014 to 2018. HAPLS, the world's first all-diode-pumped petawatt laser, is now a key component of the European Union's Extreme Light Infrastructure Beamlines facility in the Czech Republic (see "Advanced Laser Promises Exciting Applications").
"The RRL will build on the groundbreaking work that was done on HAPLS," Spinka said. "It will pair the direct chirped-pulse amplification technique used in NIF's flashlamp-pumped neodymium-doped glass Advanced Radiographic Capability with the HAPLS diode-pumped glass pump laser technology in a refined architecture developed through LLNL's Laboratory Directed Research and Development program.
"This architecture, originally dubbed the Scalable High-power Advanced Radiographic Capability, or SHARC, eliminates the lossy second (titanium-doped sapphire) stage of the HAPLS laser system," Spinka said, "ultimately delivering about five times higher energy than HAPLS at the same peak power and repetition rate."
LLNL's RRL for the MEC-U facility will be developed in parallel with performance ramping of the HAPLS (now known as L3-HAPLS) laser at ELI-Beamlines to its full design specifications. It also will leverage additional advanced laser technologies being developed by APT, including a new high-energy Faraday rotator developed under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement with Electro-Optics Technologies Inc.
Enabling new physics
"MEC-U is a core part of NIF&PS's strategy for developing next-generation high-average-power ultrafast lasers and enabling high rep-rate HED science," Tang said. "The new physics the MEC-U enables is broad-ranging and highly applicable to LLNL missions. It is an exciting opportunity for LLNL and the community."
"Not only are we working with some of the leading laser laboratories in the world," Fry added, "but we're also working with world experts in experimental science, high-energy-density science, and the operation of DOE Office of Science user facilities, where scientists from all over the world can come to do experiments."
Access to the facility will be facilitated in part by LaserNetUS, a research network that is boosting access to high-intensity laser facilities at labs and universities across the country.
MEC-U was approved by DOE's Office of Science last fall to move from the conceptual design phase to preliminary design, with construction expected to start in approximately two years.
The APT RRL team is led by Tang as the senior team lead; Spinka as project manager and chief scientist; Robert Plummer as project engineer; and Brendan Reagan as laser architect.
Provided by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory