Biological crusts affected by drought can still stabilize soils
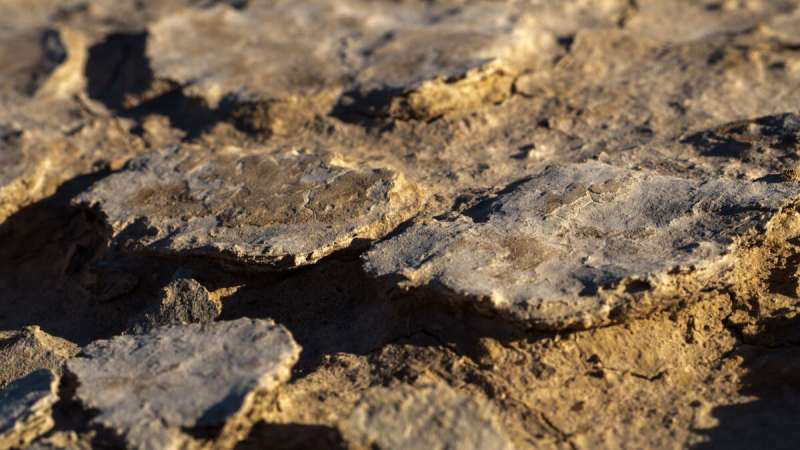

Biological soil crusts are communities of cyanobacteria, fungi, lichens, and other living organisms that can bind grains together and reduce the susceptibility of soils to erosion by water or wind. Crusts dominated by cyanobacteria, which occur naturally in many drylands, hold promise as a tool to help control erosion and restore degraded land. To date, however, most studies have focused on how individual cyanobacteria species cultured in a lab, rather than the more structurally complex natural communities, respond to changes in their environment.
To help fill this gap, Bullard et al. investigated how in situ cyanobacterial crusts in central Australia's Diamantina National Park responded to simulated precipitation in three adjacent dryland environments: sand dune, floodplain, and the area between them (nebkha). The team measured the changes in several of the environments' biological and physical characteristics—including photosynthesis, soil moisture, biological crust strength, and each substrate's wind erodibility—following rainfall simulator treatments of 5 and 10 millimeters to crusts experiencing a yearlong drought.
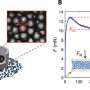
The researchers found that the cyanobacterial crusts responded rapidly to moisture, exhibiting higher levels of photosynthesis following the 10-millimeter application and displaying a more intense response when air temperatures were warmer. In addition, they found that regardless of the amount of moisture, air temperature, or substrate, the spike in photosynthesis was short-lived, returning to background levels within a day.
The wind tunnel experiments revealed that wind is more effective at eroding soil particles following 5-millimeter, rather than 0-millimeter or 10-millimeter, treatment of moisture. The authors attribute this result to the impacts of individual raindrops, which cause sand grains to shift toward the surface. When the wind blows, it entrains these loose grains, and these in turn impact others, causing erosion.
Collectively, the findings show that drought-affected cyanobacterial crusts can still protect the substrate from wind erosion at the small scales examined in this study. But climate change forecasts indicate that this region will experience more frequent and longer periods of extreme heat and longer intervals between rainstorms. These shifts are predicted to further reduce the crusts' elasticity and alter the species that compose them, potentially putting at risk their ability to stabilize soils.
More information: J. E. Bullard et al, Cyanobacterial Soil Crust Responses to Rainfall and Effects on Wind Erosion in a Semiarid Environment, Australia: Implications for Landscape Stability, Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences (2022). DOI: 10.1029/2021JG006652
Provided by American Geophysical Union
This story is republished courtesy of Eos, hosted by the American Geophysical Union. Read the original story here.