A new approach to predict stable species in liquids can guide the design of optimal solution performance
A team of researchers led by Nav Nidhi Rajput, Ph.D., at Stony Brook University, have found a way to computationally predict stable molecular species in liquid solutions. The new method, detailed in a paper in Nature Computational Science, introduces a fully automated high-throughput computational framework to predict stable species by computing their nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) chemical shifts.
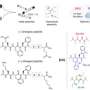
Liquid solutions are essential aspects of both materials science applications such as battery development, and biological applications such as drug discovery. However, to optimize the performance of liquid applications, an understanding of the structure and thermodynamic stability and transport of any chemical species in a solution is paramount. Rajput and colleagues used NMR as a powerful technique to develop an atomistic view to predict stable species.
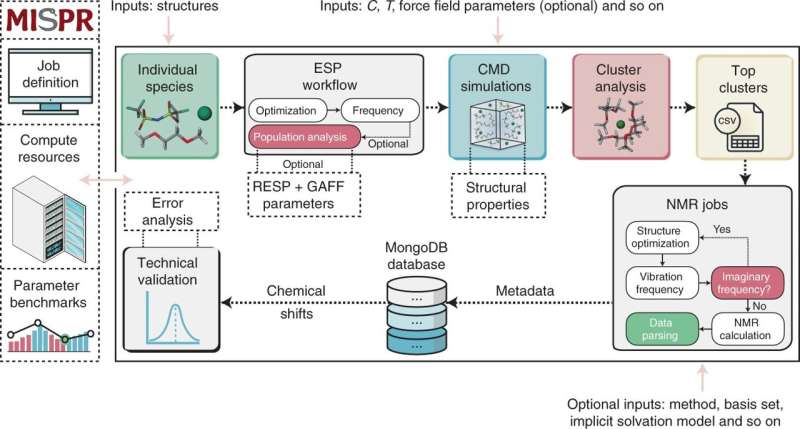
"Elucidating the complex solvation environment in multi-component liquid solutions can be a daunting task, even by using advanced experimental and computational techniques," explains Rajput, Assistant Professor in the Department of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering in the College of Engineering and Applied Sciences. "We combined density functional theory with classical molecular dynamics simulations to make our predictions via NMR."
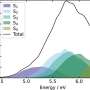
The researchers developed and tested a computational framework that through simulations robustly and efficiently calculates, analyses, and stores NMR chemical shifts from a variety of molecules in liquid solutions. They also say the framework addresses some of the most challenging aspects of computational NMR by eliminating intuition driven prediction of stable species in liquid solutions.
They add that data collected from this framework should provide fingerprints to guide future experimental investigations of liquid solutions that have optimal properties for material and science applications.
More information: Towards accurate predictions of NMR chemical shifts in liquid solutions, Nature Computational Science (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s43588-022-00204-5
Journal information: Nature Computational Science
Provided by Stony Brook University