Image: Hubble spots swirls of dust in the flame Nebula
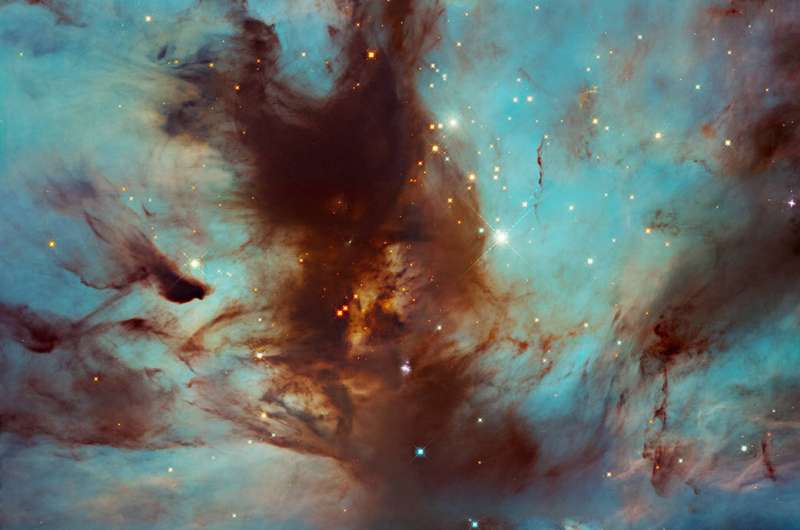

The Flame Nebula, also called NGC 2024, is a large star-forming region in the constellation Orion that lies about 1,400 light-years from Earth. It's a portion of the Orion Molecular Cloud Complex, which includes such famous nebulae as the Horsehead Nebula and Orion Nebula.
This image focuses on the dark, dusty heart of the nebula, where a star cluster resides, mostly hidden from view. Nearby (but not visible in this image) is the bright star Alnitak, the easternmost star in the Belt of Orion. Radiation from Alnitak ionizes the Flame Nebula's hydrogen gas. As the gas begins to cool from its higher-energy state to a lower-energy state, it emits energy in the form of light, causing the visible glow behind the swirled wisps of dust.
Researchers have used Hubble to measure the mass of stars in the cluster as they search for brown dwarfs, a type of dim object that's too hot and massive to be classified as a planet but also too small and cool to shine like a star.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center