Credit: Wiley
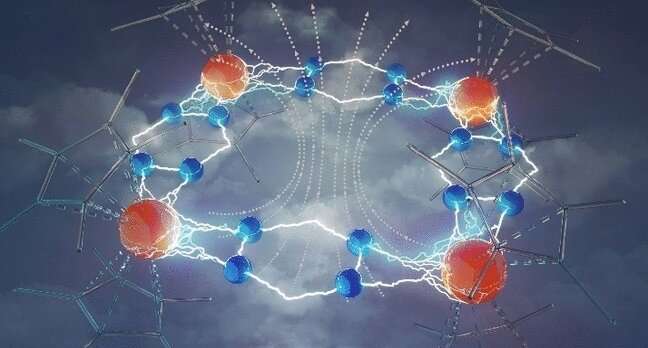
Magnets formed from a single molecule are of particular interest in data storage, since the ability to store a bit on every molecule could vastly increase the storage capacity of computers. Researchers have now developed a new molecular system with a particular magnetic hardness. The ingredients in this special recipe are rare earth metals and an unusual nitrogen-based molecular bridge, as shown in the study published in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
The suitability of a molecule to become a magnetic data storage medium is dependent on the ability of its electrons to become magnetized and to resist demagnetization, also known as magnetic hardness. Physicists and chemists build molecular magnets like this from metal ions that are magnetically coupled to one another via molecular bridges.
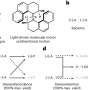
However, these coupling bridges have to meet certain criteria, such as ease of production and versatility. For example, a radical dinitrogen bridge—two nitrogen atoms with an additional electron, making the dinitrogen a radical—gave outstanding results for rare earth metal ions, but is very difficult to control and offers "no room for modification," explain Muralee Murugesu and his team from the University of Ottawa, Canada, in their study. To give them greater scope, the team enlarged this bridge using a "double dinitrogen"; the unexplored tetrazine ligand has four nitrogen atoms rather than two.
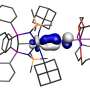
To produce the molecular magnet, the researchers combined the new tetrazine ligand with rare earth metals—the elements dysprosium and gadolinium—and added a strong reducing agent to the solution to form the radical tetrazine bridges. The new magnet crystallized in the form of dark red prism-shaped flakes.
The researchers describe the molecular unit within this crystal as a tetranuclear complex in which four ligand-stabilized metal ions are bridged together by four tetrazine radicals. The most significant property of this new molecule is its extraordinary magnetic hardness or coercive field. This means that the complexes formed a durable single-molecule magnet that was particularly resistant to demagnetization.
The team explain that this high coercive field is achieved by strong coupling through the radical tetrazine unit. The four metal centers of the molecule are coupled together to give one molecular unit with a giant spin. Only the predecessor to this molecule, with the dinitrogen bridge, gave stronger coupling. However, as already mentioned, it was also much less versatile and less stable than the new tetrazine radical bridge.
The team highlight that this method could be used to produce other multinuclear complexes with giant spin, offering superb opportunities for developing extremely efficient single-molecule magnets without the difficulties of previous candidates.
More information: Niki Mavragani et al, Radical‐Bridged Ln 4 Metallocene Complexes with Strong Magnetic Coupling and a Large Coercive Field, Angewandte Chemie International Edition (2021). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202110813
Journal information: Angewandte Chemie International Edition , Angewandte Chemie
Provided by Wiley