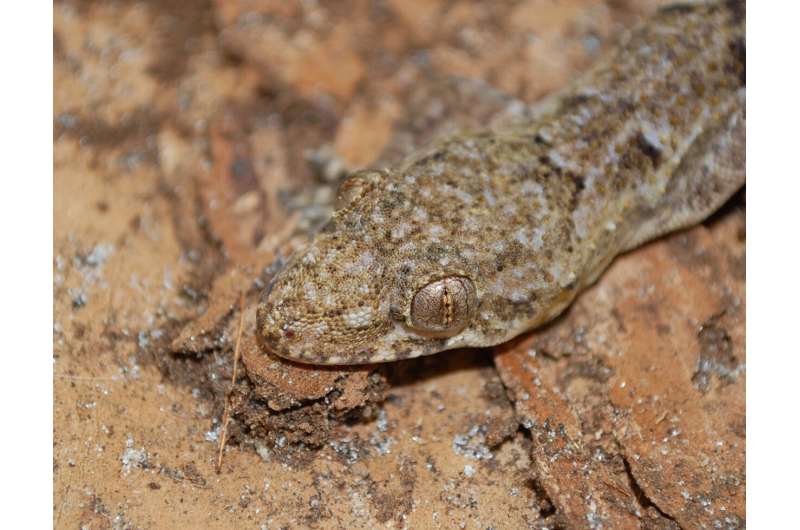
Close up of a tropical house gecko in Florida. Credit: Matt edmonds / CC BY-SA 3.0
A team of researchers from Villanova University, the Thackeray Wildlife Foundation and Museu de História Natural e da Ciência da Universidade do Porto has found evidence that the African house gecko made its way to the New World by riding aboard slave trading ships hundreds of years ago. In their paper published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, the group describes their DNA analysis of gecko specimens from around the world.
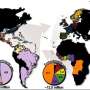
In the 1960s, two research teams published papers suggesting that the African house gecko, now considered to be an invasive species, made its way to the Americas hundreds of years ago by riding ships involved in the slave trade across the Atlantic Ocean. As its name suggests, the African house gecko is native to Africa, having originated in Mozambique and Zimbabwe. Today, the gecko is found all around the globe.
In this new effort, the researchers wondered how the African house gecko managed to spread so far and wide. To find out, they studied both its DNA and its ability to survive in different environments.
To learn more about its DNA, the team tested samples from museums around the world. In all, 186 of the geckos underwent genetic analysis and the researchers discovered approximately 20 interrelated species. But only one of those lineages managed to make its way to the Americas and to flourish—Hemidactylus mabouia. The researchers also found that the species in the Americas had undergone few genetic changes, suggesting it had not lived there for very long, perhaps just a few centuries.
The researchers also noted that H. mabouia has a characteristic that makes it better able to adjust to living in varied conditions. It inhabits wide open spaces, including human-populated areas, rather than forest or bush. It has also been found to hunt in artificial lighting conditions, which tend to attract the kinds of bugs the geckos eat.
Given the confluence of the data, the researchers suggest it that H. mabouia likely made its way to the Americas via the slave trade—a time when there were significant numbers of boats traveling between Africa and North and South America.
More information: Ishan Agarwal et al, How the African house gecko ( Hemidactylus mabouia ) conquered the world, Royal Society Open Science (2021). DOI: 10.1098/rsos.210749
Journal information: Royal Society Open Science
© 2021 Science X Network