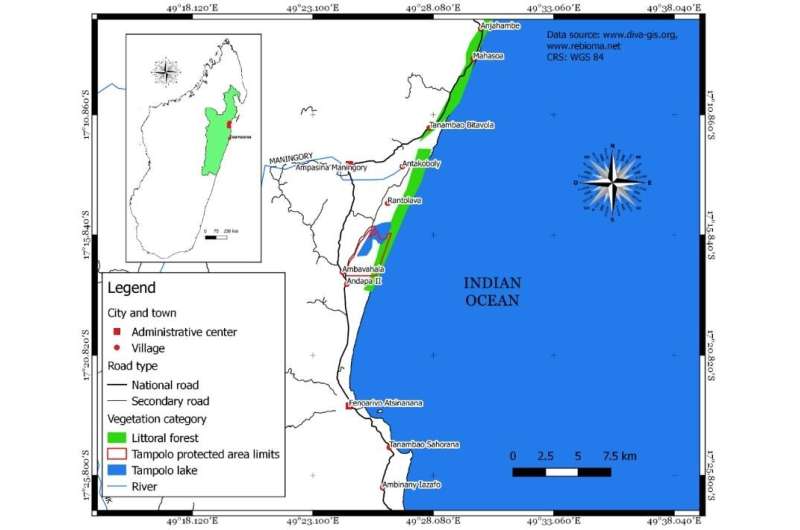
Figure 1. Map of the study area: Location of Tampolo forest and the adjacent communities living around the forest. Credit: WBG
Recently, scientists made a survey of the floristic composition of Tampolo Forest of Fenoarivo Atsinanana, Northeastern Madagascar, to document the useful forest plants with emphasis on medicinal plants, which is useful in the conservation efforts in the region's flora.
It was conducted by scientists from the Flora and Plant Taxonomy in Eastern Africa Research Group of the Wuhan Botanical Garden of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Association de Valorisation de l' Ethnopharmacologie en Régions Tropicales et Méditerra-néennes (AVERTEM), and the University of Lilles, France.
Tropical forests not only are important habitats for endangered plant and animal species, but also provide various ecosystem services, which are crucial for the local human population. Most global biodiversity hotspots are located in the tropics in developing countries, where human demographic pressure is exceptionally high. Deforestation driven by the increased land use change, natural resource overexploitation, and climate change has led to the rapid loss of the tropical forests.
Madagascar is home to about 14,000 plant species, out of 90% of which are endemic. The high degree of endemism is due to Madagascar's long isolation following its separation from Africa and India's land masses in the Mesozoic period.
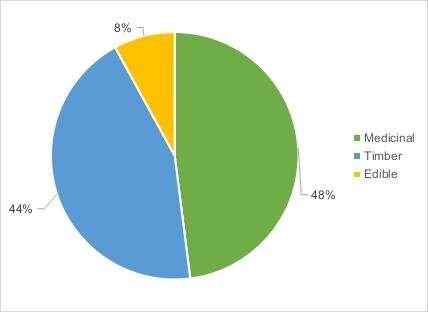
Figure 2. Graphic representation of the utilization of the plants. Credit: WBG
In this survey, 65 inhabitants between 25 and 75 years old were interviewed. 123 taxa were cited as useful in the locality, of which, 48% were used as medicine, 44% were timber and firewood, 8% were food.
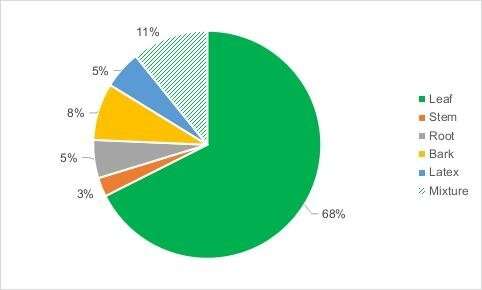
Among the useful plants, 92 taxa were exclusively from the forest and 31 were ruderal species. And medicinal plants were mostly used to cure stomachache (71%), fever (33.3%), and fatigue (25%), and leaves were the most frequently used parts (68%) that were used in the cure of most of the diseases.
Phytochemical analyses revealed the presence of active secondary metabolites which have been linked to the treatment of various diseases in the 20 selected forest taxa.
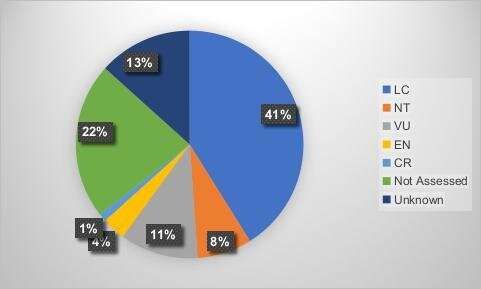
Most of the taxa (41%) collected from Tampolo forest were of least concern in conservation status, and vulnerable species and near threatened recorded 11% and 8% respectively. Whereas, one taxa, Breonia madagascariensis A. Rich. ex DC. was recorded as critically endangered.
-
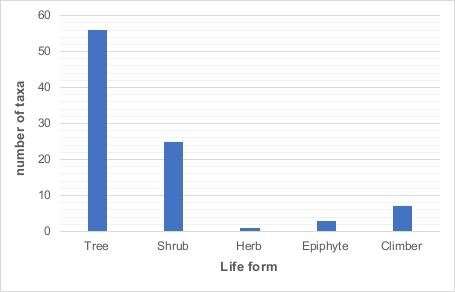
Figure 3. Distribution of taxa for each lifeform. Credit: WBG
-
Figure 4. Graphic representation of plant parts frequently used for treatment. Credit: WBG
-
Figure 5. The conservation status of the taxa collected from Tampolo forest basing on the IUCN database: LC: Least Concern; VU: Vulnerable; NT: Near Threatened; CR: Critically Endangered; EN: Endangered. Credit: WBG
-
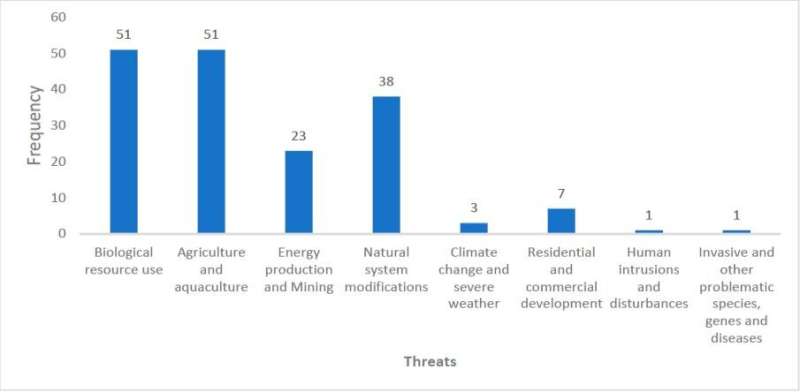
Figure 6. The most recorded threats from the IUCN database of the plant taxa. Credit: WBG
According to the scientists, younger generations are ignorant about traditional medicinal plant uses. As the older generations are fading out, a hindrance of the cultural transfer is emerging. Most of the respondents derive their daily livelihood from the forest and the activities around it (i.e. alternative source of income). Hence, combining the social and natural sciences can be useful, which comes up with sustainable ways for the conservation of natural resources.
The research entitled "Ethnobotanical Survey in Tampolo Forest (Fenoarivo Atsinanana, Northeastern Madagascar)" was published in the journal Forests.
More information: Guy E. Onjalalaina et al, Ethnobotanical Survey in Tampolo Forest (Fenoarivo Atsinanana, Northeastern Madagascar), Forests (2021). DOI: 10.3390/f12050566
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences