This image shows a research raft on Spider Lake, Wind River Indian Reservation, Wind River Range, Wyoming. Credit: Bryan Schuman, University of Wyoming
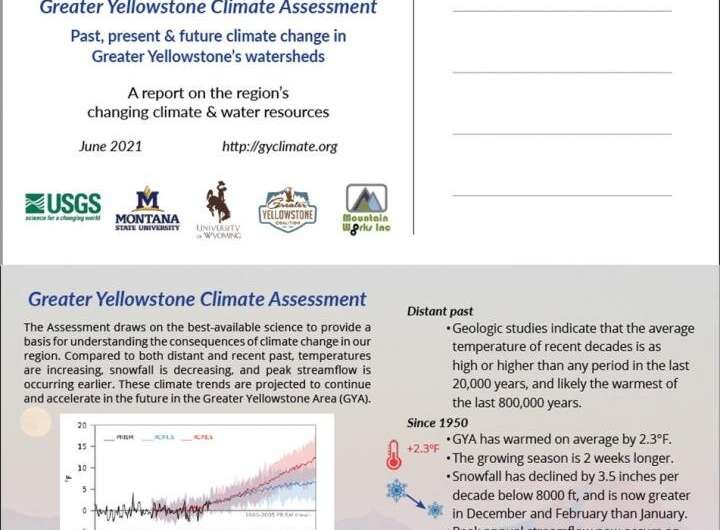
Temperature has significantly increased and snowfall decreased in the iconic Greater Yellowstone Area since 1950 because of climate change, and these trends will likely continue through the rest of the century, according to a climate report published today.
Scientists with the U.S. Geological Survey, Montana State University and the University of Wyoming studied climate change in the Greater Yellowstone Area (GYA) from 1950-2018. They evaluated how these changes could progress by 2100 based on various greenhouse gas emission scenarios and found that average GYA temperatures have increased by 2.3 degrees Fahrenheit and could increase an additional 5-10 degrees Fahrenheit by 2100.
"Greater Yellowstone is valued for its forests, rivers, fish and wildlife," said Steve Hostetler, a USGS scientist and co-lead author of the report. "The trend towards a warmer, drier climate described in this study will likely affect ecosystems in the region and the communities that depend on them."
The report also found that by the end of the century, the GYA could see:
- annual precipitation increase by 9-15%, but the combination of elevated temperatures and higher evaporation rates will likely make future conditions drier in summer;
- reduced soil moisture in the summer months, which will be an additional stress on plant communities that could make drought and wildfires more common;
- 40-60 more days per year exceeding 90 degrees Fahrenheit in Bozeman, Montana, and in Jackson, Pinedale and Cody, Wyoming, if there is little to no mitigation of future emissions.
Elk are one of many valued species in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. Credit: Bryan Shuman, University of Wyoming
"The assessment is intended to provide the best available science on past, present and future conditions in the GYA so that stakeholders have needed information to plan ahead," said Cathy Whitlock, Regents Professor Emerita of Earth Sciences at Montana State University and report co-lead author.
The report also documents the effects of climate change on the GYA over recent decades, including:
- average temperature was as high or higher than any period in the last 20,000 years and likely the warmest of the last 800,000 years, according to geologic studies;
- the growing season has increased by nearly two weeks since 1950;
- average annual snowfall has decreased by 23 inches since 1950 and measurable snow has become rare in June and September.
"The decrease in snow is due to the increase in temperature over time, which caused more precipitation to fall as rain instead of snow," said report co-author Bryan Shuman, Wyoming Excellence Chair in Geology and Geophysics at the University of Wyoming.
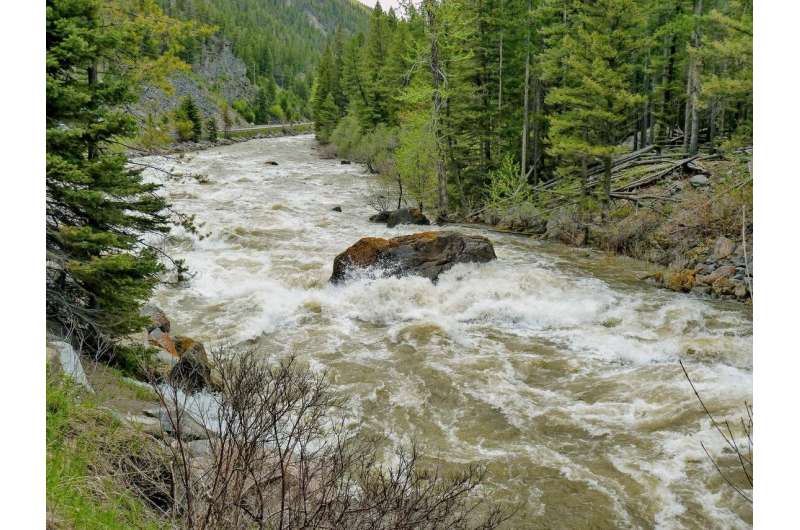
Gallatin River in flood near Big Sky, Montana, taken mid-June 2011. The USGS and partners study the effects of climate change on the Greater Yellowstone Area. Credit: Scott Bischke, MountainWorks, Inc.
The report also found that earlier snowmelt has shifted the peak streamflow eight days earlier since 1925 and reduced water supplies in summer, causing drier summer conditions that contributed to wildfires.
These ecosystem changes can impact people in the region in numerous ways, according to the scientists, including elevated temperatures and summer water shortages that affect agriculture and increased wildfires.
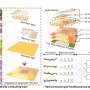
This postcard summarizes the findings from a new Greater Yellowstone Area Climate Assessment released on June 23, 2021. Credit: USGS
"Based on nearly 50 interviews with community leaders, city officials, agencies, businesses, citizens, ranchers and Tribal leaders, water and the need for more climate information are top concerns for folks in the GYA," said co-author Charles Wolf Drimal from the Greater Yellowstone Coalition.
More information: The report is available beginning June 23 at www.gyclimate.org.
Provided by United States Geological Survey