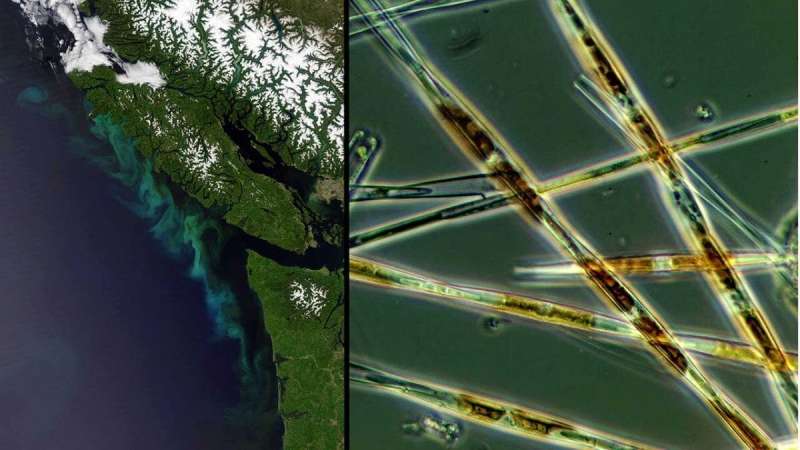
A satellite image (left) shows a bloom of the harmful algal species Pseudo-nitzchia off the coast of Washington State and British Columbia. Harmful algal blooms like these can shut down economically important shellfisheries for months. Credit: NASA (left) and NOAA Northwest Fisheries Science Center (right))
The first-ever global statistical analysis of trends in harmful algal blooms (HABs) has shown that, worldwide, there is no significant increase in HABs events, but that in some regions, events that include toxic species of algae affecting humans and wildlife are on the rise. In addition, the study finds that human activity, primarily aquaculture in coastal waters, and the economic impacts that HABs event cause to the fast-growing growing industry, is likely behind the perceived increase.
The study, which appears in Communications Earth & Environment was led by Gustaaf Hallegraeff at the University of Tasmania and included Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) biologist and director of the U.S. National Office for Harmful Algal Blooms Don Anderson, along with scientists from 14 countries.
"The 2019 report by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) suggested that the occurrence and toxicity of blooms will increase in the future," said Hallegraeff. "But these trends remain an open debate."
"There has been a lot of speculation in recent years about whether HABs are increasing due to climate change or changes in land use or aquaculture," said Anderson. "This should put the general debate to rest, but it also highlights places where we could be doing more to address the problem, which is clearly a growing threat in many regions, and to better predict future trends."
Harmful algae encompass a wide range of plankton species, many of which produce toxins that can cause paralysis, neurological disorders, amnesia, gastro-intestinal illness, skin and respiratory irritation, and even death. Symptoms can affect humans, as well as marine and freshwater wildlife, such as marine mammals, shellfish, fish, and seabirds, including many economically important animals. Other species of harmful algae grow rapidly in the presence of warm water, high nutrients, and other environmental conditions, resulting in a number of "nuisance" effects, such as clogged water and sewer systems, fouled beaches, and low dissolved oxygen levels leading to fish die-offs. Both toxic and nuisance HAB events appear to be on the rise worldwide, but there have long been questions about whether this perception is well-founded or is due to increased monitoring efforts or more varied and costly impacts of blooms.
To better understand HAB trends globally and regionally, the research team analyzed data from a worldwide database of HAB events known as HAEDAT (Harmful Algal Event Database), which contains 9,500 records of blooms between 1985 and 2018. Because HAEDAT only lists documented events of varying severity, the researchers also analyzed data from OBISI (Ocean Biodiversity Information System), a database of micro-algae observations worldwide, to help them determine whether the increase in HAB events was the result of steadily increasing monitoring efforts over the years and in many parts of the world.
Using nearly six million OBIS data records over the study period as a proxy for monitoring effort, they found no statistical significance to the slight upward trend in HAB events worldwide that remained after correcting for the increased number of measurements that occurred over the same period. They did, however, find statistically significant increases in six regions: Greenland, the Caribbean, the west coast of North America, Southeast Asia, the Mediterranean, and western and northern Europe. They also found statistically significant, region-specific increases of certain toxic and nuisance events, including amnesic and paralytic shellfish toxin outbreaks among marine mammals in the Arctic Pacific, Ciguatera poisoning in the Canary Islands, and red and green algae blooms in the Indian Ocean and Southeast Australia, among others.
During the study period, aquaculture production worldwide rose nearly 16-fold, and the authors found that all regions with suitable HAEDAT data reported more events as aquaculture expanded. The authors point out that increased use of coastal waters for aquaculture has been a key driver for occasionally disastrous, long-lasting economic impacts of blooms and has, in turn, driven awareness of new harmful algal species and new toxin types. This rise in aquaculture has also resulted in better management of marine resources in many instances that serve to reduce the economic and health impacts of a bloom.
"Improving efforts to monitor specific locations and for specific harmful algal species offers the prospect of better HAB prediction in the long run," said Hallegraeff. "This could bring with it greater insight into future changes, which will bring with it better seafood security."
"HABs sit at the crossroads of many societal, environmental, and scientific trends," said Anderson. "So when it comes to understanding the driving forces behind the diverse array of HABs we see, only better monitoring and more consistent data will help us manage HABs and minimize their complex impacts on society and the environment."
More information: Perceived global increase in algal blooms is attributable to intensified monitoring and emerging bloom impacts. Commun Earth Environ 2, 117 (2021). doi.org/10.1038/s43247-021-00178-8
Journal information: Communications Earth & Environment
Provided by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution