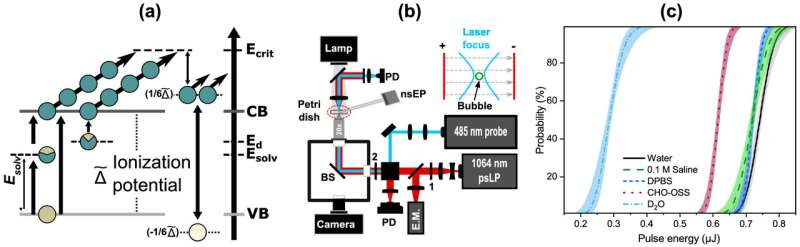
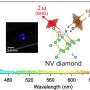
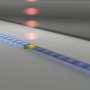
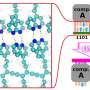
Fig. 1. Experimental design. (a) Tentative band structure of biological solution and plasma dynamics during the optoelectrical breakdown process. (b) Schematic representation of opto-electrical breakdown setup for bubble formation and detection with red indicating 1064 nm beam path and cyan indicating 485 nm probe beam path. Abbreviations indicate polarizing beam splitter cube (PBS), beam splitter (BS), pulse energy meter (E.M.), dichroic beam splitter (DBS), 750 nm short-pass filter (SPF), and photodiode (PD). Numbers 1 and 2 indicate respectively half-wave plates and 20×0.420×0.4 NA microscope objective. (c) Probit analysis curves and 95% confidence intervals of breakdown threshold (
Vladislav Yakovlev, professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M University, is part of a multiuniversity team researching how electrical and optical pulses can benefit cell absorption of materials, including vaccines.
The team investigated the optical and electrical breakdown of materials. Those effects, which describe material modification in the presence of extreme optical or electrical fields, have been studied since the 1950s. However, the simultaneous application of optical and electrical fields, especially to biologically relevant systems, hasn't been explored before.
Yakovlev said by investigating the synergistic action of electrical and optical pulses, the researchers were able to promote highly localized breakdown while reducing the threshold for such breakdown.
The newly discovered synergistic effect is particularly important if there is a need to selectively disrupt cellular membrane in a highly localized manner.
Typically, electroporation, a technique that applies an electrical field to cells to increase the permeability of the cell membrane, is used. Alternatively, an optoporation, which uses ultrashort laser pulses to form a small hole in the cell membrane, can be employed. A powerful combination of electroporation and optoporation can provide the benefits of both approaches, leading to new ways drugs and vaccines can be delivered to cells and tissues.
"One of the impacts of paramount significance of this effect, which can be of great interest to a general audience, is improved accuracy of vaccine delivery for COVID-19," the team said in an impact statement.
The team recently published a paper in the journal Photonics Research. The research is funded by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, with Sofi Bin-Salamon serving as project manager.
While this technology would be a new addition to a laboratory, the research team noted that creating the effect doesn't require sophisticated equipment, allowing it to be used in a broad range of facilities.
"We believe that a unique combination of a new fundamental science and a broad range of high-impact applications. ranging from extreme light-matter interactions to nano- and biotechnology, would be of great interest for a broad audience," Yakovlev said.
More information: Zachary N. Coker et al. Synergistic effect of picosecond optical and nanosecond electrical pulses on dielectric breakdown in aqueous solutions, Photonics Research (2021). DOI: 10.1364/PRJ.411980
Provided by Texas A&M University