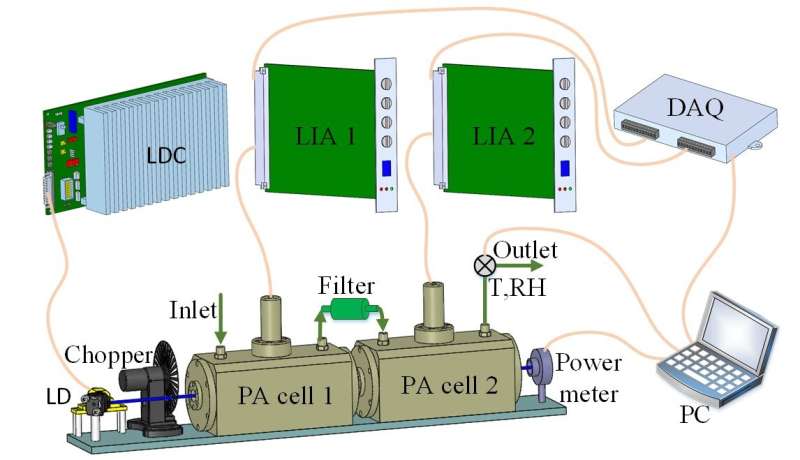
Experimental setup of the D-PAS. Credit: LIU Kun
Recently, Prof. Gao Xiaoming's group from the Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics (AIOFM) of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) designed and manufactured a photoacoustic spectroscopy-based sensor to measure aerosols and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) simultaneously.
Atmospheric aerosols and NO2 are considered main pollutants in the air, while the online measurement of aerosol absorption characteristics still poses many challenges. Since the photoacoustic spectroscopy (PAS) is not affected by light scattering and the acoustic transducer is not limited by the wavelength of light, it has unique advantages in the measurement of aerosols and trace gases.
"This PAS (D-PAS) is based on a 443 nm laser diode," explained Prof. LIU Kun, member of the research team. "By optimizing the structure of acoustic resonator, we realized high sensitivity and large flow rate for online measurement of aerosol absorption and NO2."
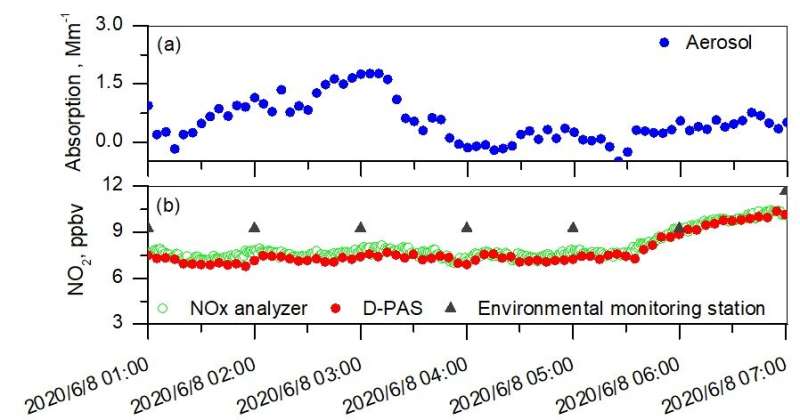
During the experiment, both the intercomparison and consistency between the developed D-PAS and commercial NOX analyzer when measuring NO2 in the atmosphere proved the reliability of this novel D-PAS sensor.
With important potential applications in the development of aerosol absorption and NO2 analysis, this sensor can be applied to the field of atmospheric measurement or environmental monitoring.
-
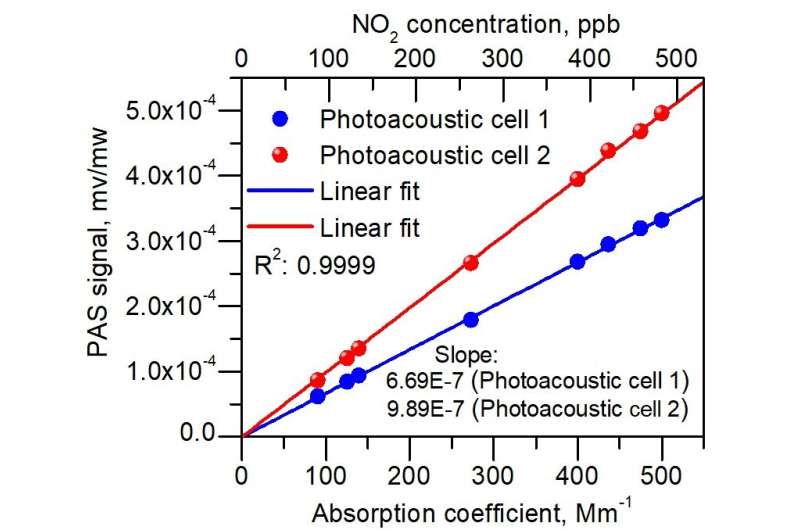
Calibration results of the developed D-PAS. Credit: LIU Kun
-
Time series measurements of aerosol absorption coefficient and NO2 concentration. Credit: LIU Kun
More information: Yuan Cao et al. Development of a 443 nm diode laser-based differential photoacoustic spectrometer for simultaneous measurements of aerosol absorption and NO2, Photoacoustics (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100229
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences