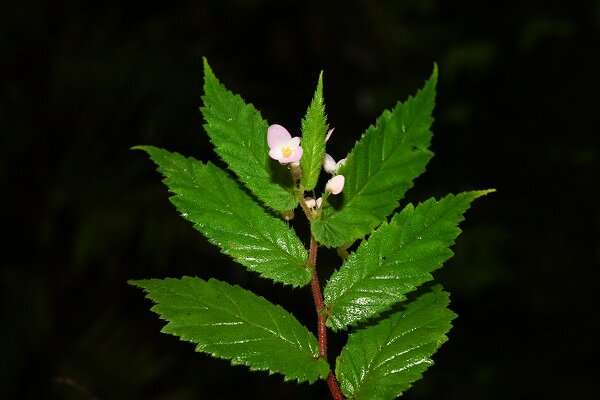
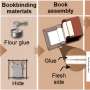
Begonia depingiana. Credit: DING Hongbo
Begonia comprises the sixth-largest genus of angiosperms and the number of accepted species of Begonia currently reaches more than 1,991 species. In China, about 221 species have been recorded according to the Flora of China.
During the botanical surveys from 2019 to 2020 in Yunnan, researchers from the Xishuangbanna Tropical Botanical Garden (XTBG) collected an unknown Begonia species.
After careful taxonomical studies of the genus, and comparison of this unknown species with similar species, the researchers confirmed that it is a new species of Begonia. They named it as Begonia depingiana and published their findings in Phytotaxa.
Begonia depingiana has tuberous habit, alternate leaves, three stigmas, a three-locular ovary and bifid placenta. It is similar to B. namkadingensis in its tuberous habit and the tepal number of the male and female flower, but significantly differs by its higher number of stamens, three stigmas, and three-locular ovary.
Begonia depingiana also resembles B. pellionioides in pinnate leaf venation, but differs by its shorter plant, tuberous rootstock and densely pinkish-white ciliate ovary.
Begonia depingiana is endemic to Jinggu County, Yunnan Province. It was found on rocky slope in a coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest area at about 1,200 meters in elevation. It is currently known at the type locality.
Thousands of individuals have been found, but this area remains outside of protected areas. The habitat is close to the road and vulnerable to disturbance by human activity, and it might be lost to road construction in the coming years. It also could be threatened due to over-collecting by plant hunters seeking ornamental plants. Therefore, its conservation status may be Critically Endangered (CR) in the future.
More information: HONG-BO DING et al. A new tuberous species of Begonia, L. (Begoniaceae) from southern Yunnan, China, Phytotaxa (2020). DOI: 10.11646/phytotaxa.474.1.8
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences