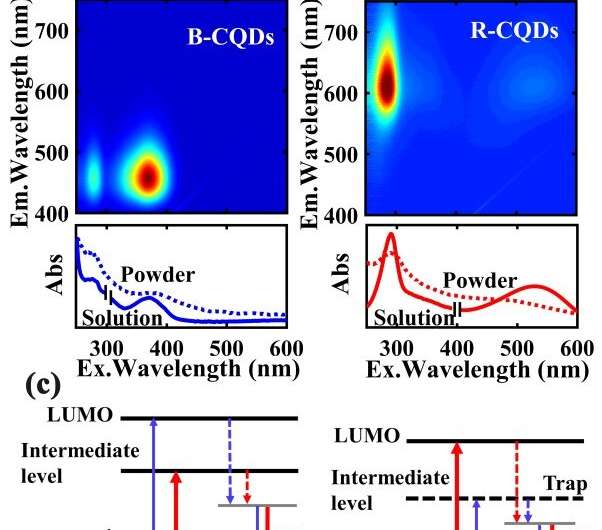
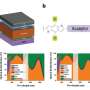
Fig.1. PL and UV-Vis absorption spectra are shown in (a) for B-CQDs and in (b) for R-CQDs. (c) The diagram of the energy levels and the electronic transition channels for PL emission from B- (left panel) and R-CQDs (right panel). Credit: SONG Dan
Recently, researchers led by Prof. XU Wen from the Institute of Solid State Physics of the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS), along with their collaborators from the Southwest University in Chongqing, applied the Terahertz time domain spectroscopy (THz TDS) to study the optoelectronic properties of fluorescent carbon quantum dots (FQCDs).
Carbon quantum dots (CQDs) are a class of zero-dimensional carbon materials, which have drawn great attention due to their outstanding optical and optoelectronic properties. It is an environmental-friendly material promising for realization of full-color lighting and displays, in which case, the FCQDs should be used in solid state.
This time, the research group prepared two kinds of FCQDs, which could emit bright blue (B-CQDs) and red (R-CQDs) lights in solutions under optical excitation.
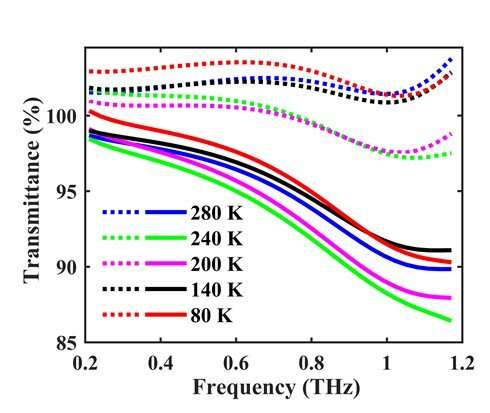
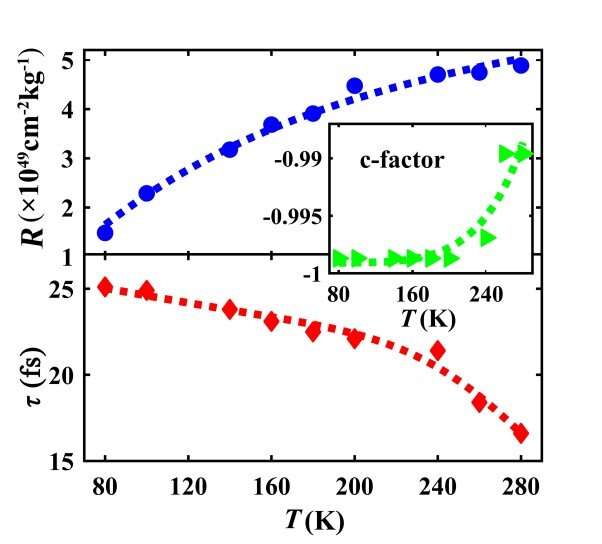
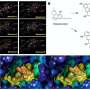
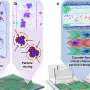
After studying the THz optoelectronic response of dry FCQD particles with temperature range from 80 to 280 K, they found that R-CQDs behaved like an optical insulator in 0.2—1.2 THz range, while B-CQDs experienced insulator-to-semiconductor transition with increasing THz radiation frequency and temperature. Optical conductance and key physical parameters of FCQDs could be deduced from THz transmittance spectra.
These results explain the mechanism of this phenomenon and would lead to more sufficient understanding of the basic physical properties of FCQDs.
This is the first time scientists applied the THz TDS to the investigation of dry CQDs. And an interesting phenomenon of insulator-to-semiconductor transition in FCQDs in THz bandwidth was observed experimentally, indicating that the CQDs can be utilized to realize the advanced THz optoelectronic materials and devices.
-
Fig. 2. Spectra of the transmittance induced by R-CQDs (dotted curves) and B-CQDs (solid curves) at different temperatures as indicated. Credit: SONG Dan
-
Fig.3. The carrier density related parameter R=gne/m* (upper panel), the carrier relaxation time τ (lower panel) and the carrier localization factor c (inset) as a function of temperature for B-CQDs. The symbols are obtained via fitting the experimental results with the DSF, the curves are given with theory fitting. Credit: SONG Dan
More information: Dan Song et al. Optically induced insulator-to-semiconductor transition in fluorescent carbon quantum dots measured by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy, Carbon (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.075
Journal information: Carbon
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences