Effects of organohalogen pollution are coded in hepatic gene expression profiles of Baltic salmon
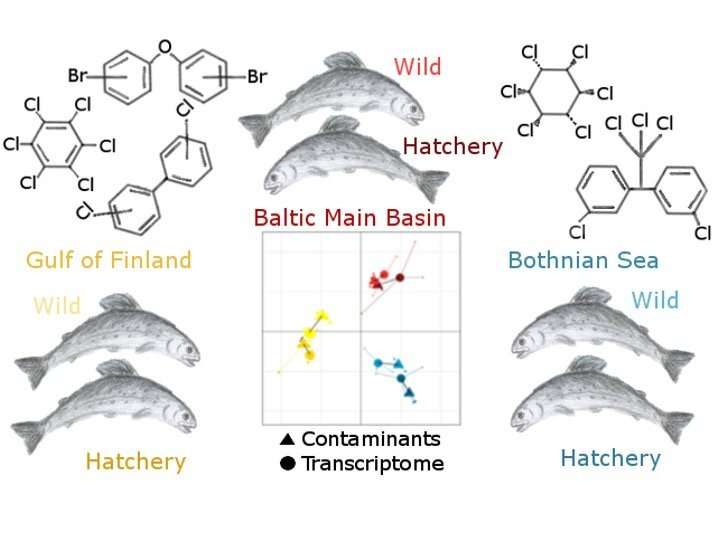
Researchers of Ehime University and the University of Helsinki measured hepatic organohalogen (OHC) concentrations and gene expression profiles in Atlantic salmon collected from three areas in the Baltic Sea. The results showed that OHCs and gene expression profiles were individually grouped in three areas and the covariation of the two datasets provided by a multivariate method was significantly similar. This suggests that the gene expression profiles in salmon are affected by OHC contamination.
Hatchery-reared Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) have been released to support the wild salmon stocks in the Baltic Sea for decades. During their feeding migration, salmon are exposed to organohalogen compounds (OHCs). Here, we investigated the OHC levels and transcriptome profiles in the liver of wild and hatchery-reared salmon collected from the Baltic main basin, the Bothnian Sea, and the Gulf of Finland and examined whether salmon origin and OHC levels contributed to the hepatic transcriptome profiles. There were no differences in the OHC concentrations and transcriptome profiles between wild and hatchery-reared fish but there were large differences among the areas. Several transcript levels were associated with polychlorinated biphenyls, chlordanes, and dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane in a concentration-dependent manner. When comparing the different areas, lipid metabolism, environmental stress, cell growth and death-related pathways were enriched in the liver transcriptome. Coinertia analysis, a multivariate method, showed that the covariation in the OHC levels and the transcriptome were significantly similar. These results suggest that the hepatic transcriptomes in wild and hatchery-reared salmon are more affected by the OHC level than the salmon's origin.
This paper was published in Environmental Science and Technology on November 9, 2020.
More information: Mirella Kanerva et al. Effects on the Liver Transcriptome in Baltic Salmon: Contributions of Contamination with Organohalogen Compounds and Origin of Salmon, Environmental Science & Technology (2020). DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04763
Journal information: Environmental Science and Technology , Environmental Science & Technology
Provided by Ehime University