Chinese astronomers discover 591 high-velocity stars with LAMOST and Gaia
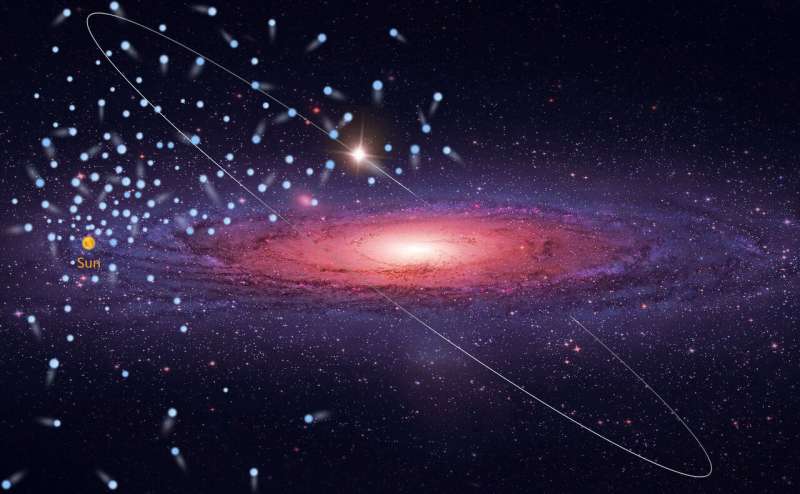

A research team, led by astronomers from National Astronomical Observatories of Chinese Academy of Sciences (NAOC), has discovered 591 high velocity stars based on data from the Large Sky Area Multi-Object Fiber Spectroscopic Telescope (LAMOST) and Gaia, and 43 of them can even escape from the Galaxy.
The study was published online in The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series on Dec. 17.
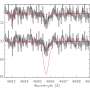
After the first high-velocity star was discovered in 2005, over 550 ones have been discovered with multiple telescopes in 15 years. "The 591 high-velocity stars discovered this time doubled the total number previously discovered, bringing the current total number exceeding 1,000," said Dr. Li Yinbi, lead author of the study.
High-velocity stars are kind of fast-moving stars, and they can even escape from the Galaxy. "Though rare in the Milky Way, high-velocity stars, with unique kinematics, can provide deep insight into a wide range of Galactic science, from the central supermassive black hole to distant Galactic halo," said Prof. LU Youjun from NAOC, a co-author of this paper.
LAMOST, the largest optical telescope in China, has the highest spectral acquisition rate in the world and can observe about 4,000 celestial targets in one single exposure. It began regular surveys in 2012, and established the largest spectra database in the world.
Gaia is a space-based mission in the science program of the European Space Agency (ESA) launched in 2013. It provided astrometric parameters for over 1.3 billion sources, which is the largest database of astrometric parameters. "The two massive databases provide us unprecedented opportunity to find more high-velocity stars, and we did it," said Prof. Luo Ali from NAOC, a co-author of this research.
From the kinematics and chemistries, the research team found that the 591 high-velocity stars were inner halo stars. "Their low metallicities indicate that the bulk of the stellar halo formed as a consequence of the accretion and tidal disruption of dwarf galaxies," said Prof. Zhao Gang from NAOC, a co-author of the study.
The discovery of these high-velocity stars tells us that the combination of multiple large surveys in the future will help us to discover more high-velocity stars and other rare stars, which will be used to study the unsolved mystery about our Galaxy.
More information: Yin-Bi Li et al. 591 High-velocity Stars in the Galactic Halo Selected from LAMOST DR7 and Gaia DR2, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series (2020). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4365/abc16e Yin-Bi Li et al. 591 High-velocity Stars in the Galactic Halo Selected from LAMOST DR7 and Gaia DR2, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series (2020). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4365/abc16e
Journal information: Astrophysical Journal Supplement
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences