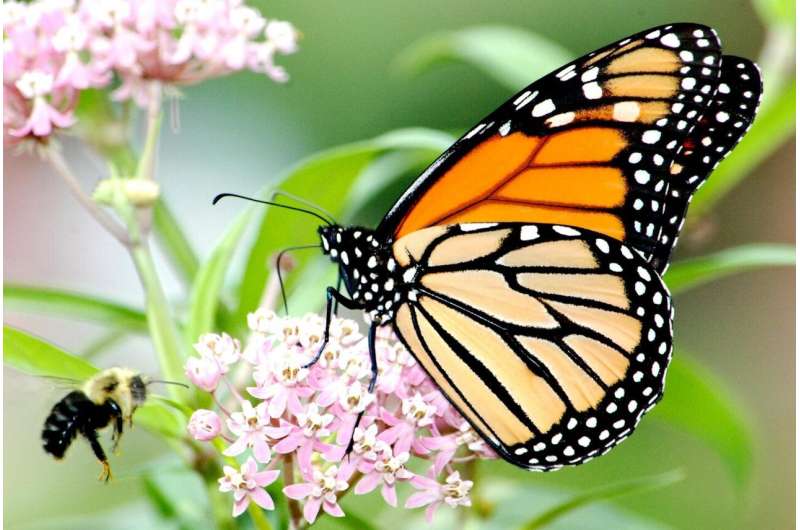
A monarch butterfly and a bee visit a milkweed plant. Credit: Jim Hudgins, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Plant cultivars are natural variants of native plants that have been deliberately collected, selected, cross-bred or hybridized for desirable traits that can be maintained through propagation. Although experts generally discourage using cultivars for ecological restoration in natural habitats such as forests and wetlands, consumers find them attractive when seeking new plants that combine the attributes of natives and ornamentals. For the nursery industry, cultivars open the door to new introductions and vast market potential. Indeed, most native plants sold at most garden centers are available only as cultivars as opposed to true or ''wild type'' native species.
Researchers Adam Baker and Daniel Potter from the University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment set out to study whether or not native milkweed cultivars, planted by 'citizen ecologists', were effective in helping to support the declining monarch butterfly populations.
"Native milkweed cultivars including those selected for novel floral display, longer blooming duration, compact growth form and other consumer-attractive traits are increasingly available in wholesale nurseries and at local garden centers," said Baker. "It is important to determine whether these cultivars have the same ability as wild-type native plants to attract monarchs and bees and contribute to effective ecological gardens."
In the study, Baker, Potter and their collaborators planted six urban gardens each containing two species of native wild-type milkweeds (swamp and butterfly), along with three cultivars of each species. They monitored them for monarch and bee visitation for two summers. In both years, monarchs laid many more eggs on swamp milkweed than on butterfly milkweed, despite both species being equally suitable food for the caterpillars. Importantly, in both milkweed species, they found the native cultivars were just as attractive and suitable for monarchs as the respective wild-type counterparts from which those cultivars were derived.
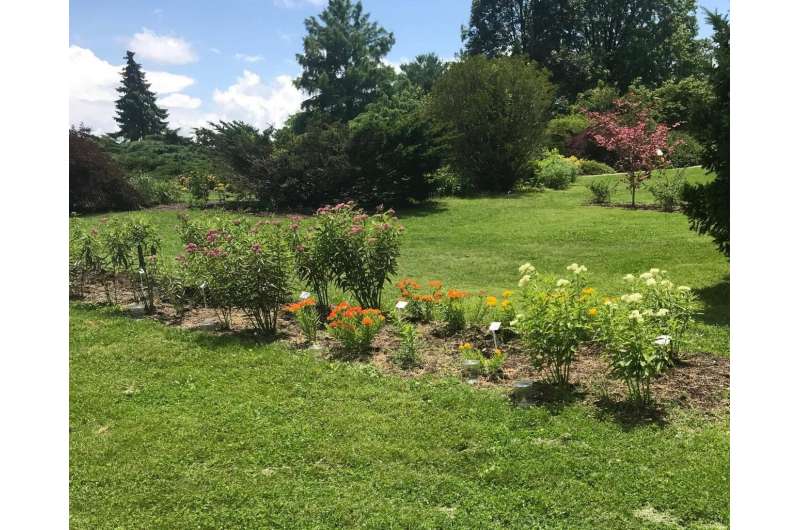
One of the six experimental gardens showing variation in height, form, and bloom color among the native milkweed species and cultivars Credit: Daniel Potter
"Previous research has shown that monarch butterflies tend to lay more eggs on taller milkweeds than on shorter ones," Potter said. "We think that is what has happened in our study because swamp milkweed is significantly taller than butterfly milkweed, and probably easier for the egg-laying female monarchs to find."
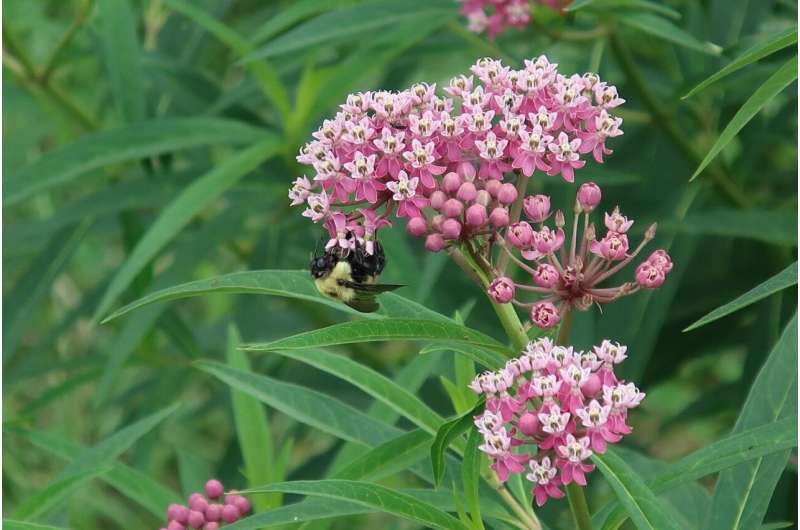
A native bumble bee sips nectar from a swamp milkweed cultivar. Credit: Daniel Potter
Milkweeds produce a lot of nectar, so besides monarchs they also attract and help to sustain native bees, honeybees, various butterflies and many other nectar-feeding insects. In the study, the scientists identified more than 2,400 bees, representing five bee families and 17 genera, visiting the milkweeds while they were in bloom. They found that swamp milkweed and its cultivars attracted proportionately more large bees, including bumble bees, carpenter bees, and honeybees, whereas butterfly milkweeds attract proportionately more small native bees. Importantly, within each native milkweed species, the cultivars attracted similar bees as their native counterparts.
These findings suggest that the efforts of individual gardeners to plant milkweed, either wild-type native plants or native cultivars, can be helpful in supporting the declining populations of both monarch butterflies and other insects.
More information: Adam M. Baker et al, Suitability of native milkweed (Asclepias) species versus cultivars for supporting monarch butterflies and bees in urban gardens, PeerJ (2020). DOI: 10.7717/peerj.9823
Journal information: PeerJ
Provided by PeerJ