Achieving distributed directional listening with fiber acoustic sensing
Recently, a research team from the Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) proposed multi-source aliasing suppression for distributed fiber acoustic sensing (DAS) with directionally coherent enhancement technology. The results were published in Optics Letters.
DAS has some unique advantages, including large coverage, high spatial-and-temporal resolution, and strong ambient adaptability, so it is widely applied in many fields.
At present, DAS is still troubled by the aliasing problem from multiple adjacent sources due to its physical mechanism. On the one hand, weak target signals may be submerged by intense broadband environmental noise; on the other hand, multiple target signals are challenging to detect individually.
The solving of multi-source aliasing is helpful to individually detect multi-source signals, the identification ability and reliability of DAS will be improved, and the large-scale application process can be promoted.
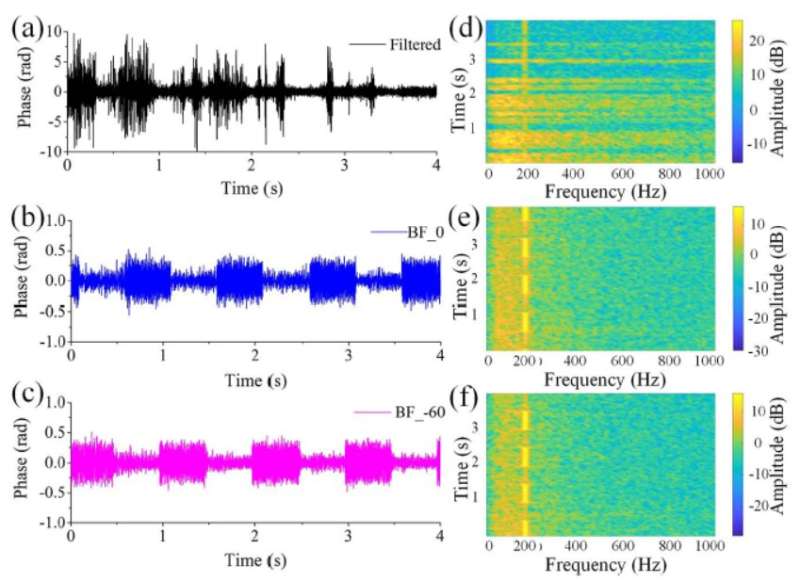
The researchers proposed a new DAS detection scheme based on distributed directional coherence enhancement for multi-source interference suppression.
With the unique continuously spatially detection characteristic and array signal processing idea, the spatial correlation of multi-dimension detection data was explored, the distributed directional coherence enhancement was realized, signals from specific directions could be enhanced or suppressed, and multi-source aliasing could be suppressed.
In experiments, they found the proposed method can extract weak target signals from intense broadband ambient noise. The same-frequency signals from different adjacent targets can also be separated from each other with the directional listening method.
In the proposed method, the array signal processing idea was successfully utilized into DAS, and distributed directional listening was realized. Many common problems from multi-source aliasings, such as low recognition accuracy and robustness, can be resolved, and the proposed method is expected to promote the large-scale implementation of DAS.
More information: Zhaoyong Wang et al. Multi-source aliasing suppression for distributed fiber acoustic sensing with directionally coherent enhancement technology, Optics Letters (2020). DOI: 10.1364/OL.404736
Journal information: Optics Letters
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences