Tiger, pangolin farming in Myanmar risks 'boosting demand'

Conservationists have warned a sudden change in Myanmar's law allowing the commercial farming of tigers, pangolins and other endangered species risks further fuelling demand in China for rare wildlife products.
The Southeast Asian nation is already a hub for the illegal trafficking of wildlife, a trade driven by demand from neighbouring China and worth an estimated $20 billion worldwide.
In June, Myanmar's Forest Department quietly gave the green light to private zoos to apply for licences to breed 90 species, more than 20 of which are endangered or critically endangered.
It was an unexpected move that caught conservation groups off-guard but was explained by the Forest Department as a way to help reduce poaching of wild species and illegal breeding.
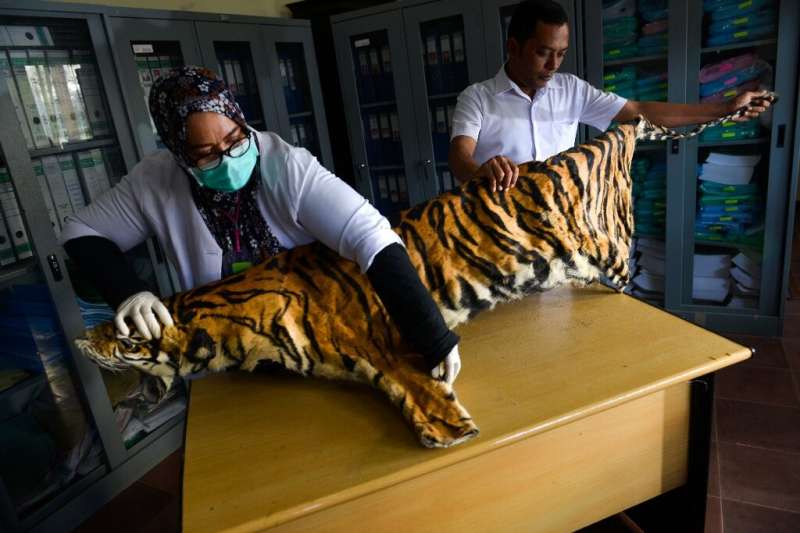
Tigers—thought to number just 22 in Myanmar—pangolins, elephants and various vulture species as well as the critically endangered Ayeyarwady dolphin and Siamese crocodile can now also be bred for their meat and skin.
But conservationists say commercial farming in the long-term legitimises the use of endangered species and fuels market demand.
"Commercial trade has been shown to increase illegal trade in wildlife by creating a parallel market and boosting overall demand for wild animal products," conservation groups WWF and Fauna & Flora International (FFI) said in a joint statement.
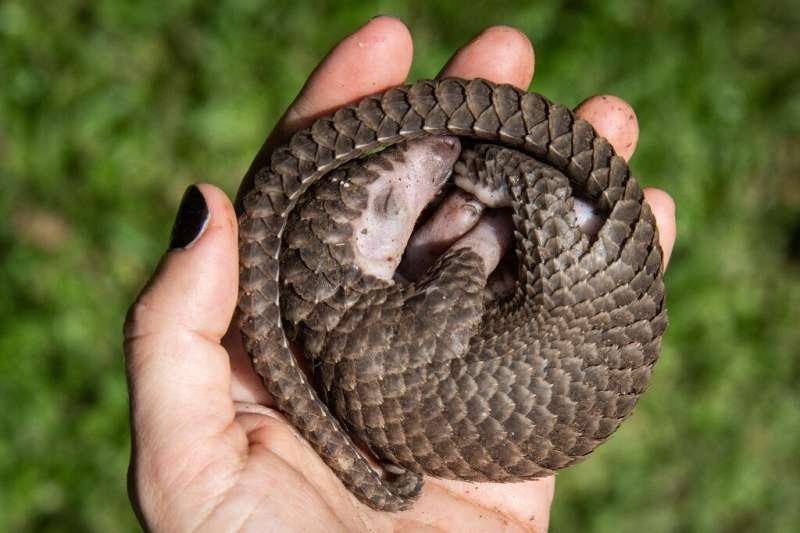

Experts also fear Myanmar's lack of capacity to regulate the trade raises the risk of disease spillover to humans from animals and even the "next COVID-19".
John Goodrich from global wild cat conservation organisation Panthera warned farming can also "provide a means for laundering wild specimens", complicating efforts to police the trade.
CITES (the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species) does allow captive breeding of certain endangered species, but only under strict regulation.
But Myanmar's ability to police the trade is disputed, say environmental groups, who fear the country risks following in the footsteps of Thailand, Laos and Vietnam, which have lost much of their wildlife.
The Forest Department said the new list was drawn up "in full adherence with the law" and after consultation with "conservation groups, academics, and experts in the field".
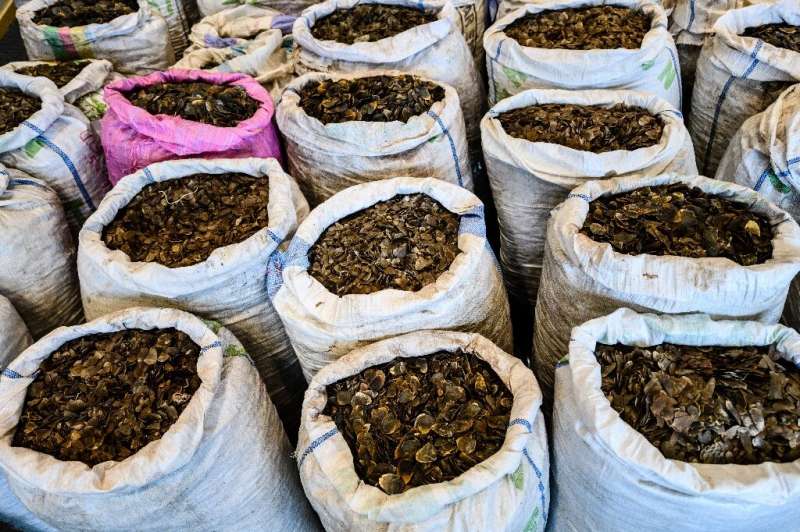

Conservationists fear the rule change risk undermining all the progress Myanmar had made in recent years to end the illegal wildlife trade.
Rare footage caught by FFI camera traps showed the "treasure trove" of species in Myanmar's forests, the group said.
"We must do everything we can to protect them."
© 2020 AFP