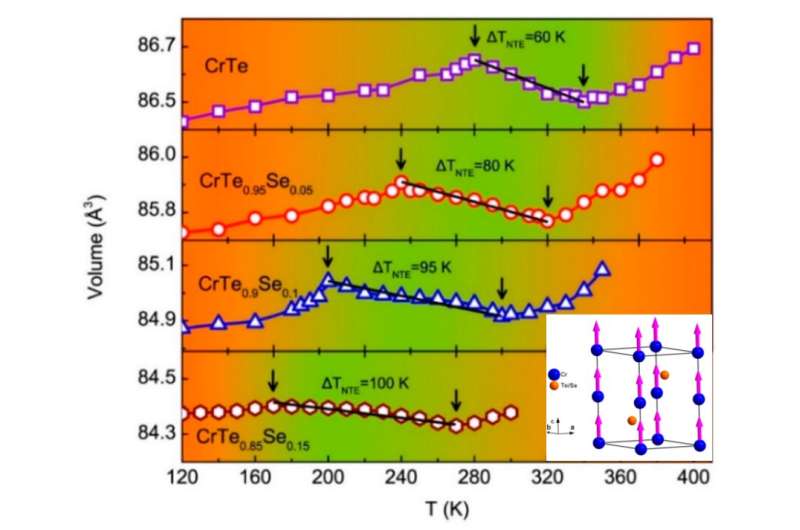
Temperature dependence of volume changes of Cr-Te-Se with different compositions. Credit: ZHENG Xinqi
Researchers used a variable temperature X-ray diffractometer (XRD) at China's Steady High Magnetic Field Facility (SHMFF) under Hefei Institutes of Physical Science and have found large linear negative thermal expansion in intermetallic Cr-Se-Te Compounds. This research was published in Inorganic Chemistry.
Generally, most materials expand upon heating and contract on cooling. However, there are some materials exhibiting contraction upon heating rather than expansion, so called negative thermal expansion (NTE).
In recent decades, NTE materials have attracted great attention because they can be used to control the coefficient of expansion when composited with the positive thermal expansion materials. In this way, even zero thermal expansion materials can be realized, the volume of which is independent of the temperature. Due to important applications in aerospace, machinery parts, printed circuit boards, and high-precision optical mirrors, NTE materials have been extensively investigated.
The magnetic intermetallic compound CrTe possesses a high Curie temperature (Tc) of about 340 K, varying with different amounts of Cr vacancy. CrTe can keep its NiAs-type structure only when the atomic fraction of Te is between 52.4% and 53.3%, indicating that it is necessary for the Cr vacancy to hold the NiAs-type structure. Its lattice parameter deviates from normal thermal expansion law, together with an obvious NTE of volume in the temperature range near Tc.
Recently, the correlation between lattice parameters and magnetic properties has been found to originate from the strong mixing bond between the nearest neighbor Cr and Te atoms.
In this work, the researchers from University of Science and Technology, Beijing and Peking University investigated the NTE properties by substituting Te with Se, which could effectively modulate NTE properties.
With the help of the XRD at SHMFF, it was able to precisely detect the variation of the lattice constant in Cr-Te-Se compounds. "A large linear NTE was obtained in magneto elastic CrTe1-xSex compounds from x=0 to x=0.15, and the NTE temperature range was also expanded by the substitution," said Zhang Xinqi, first author of this paper, also an associate professor of the University of Science and Technology Beijing.
"We also analyzed the relationship between tunable NTE and magnetic properties, and the NTE in CrTe1-xSex compounds was shown to originate from the magneto volume effect. These results are meaningful for understanding the NTE mechanisms," said Zhang Xinqi.
More information: Jiawang Xu et al. Large Linear Negative Thermal Expansion in NiAs-type Magnetic Intermetallic Cr–Te–Se Compounds, Inorganic Chemistry (2020). DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c01048
Journal information: Inorganic Chemistry
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences