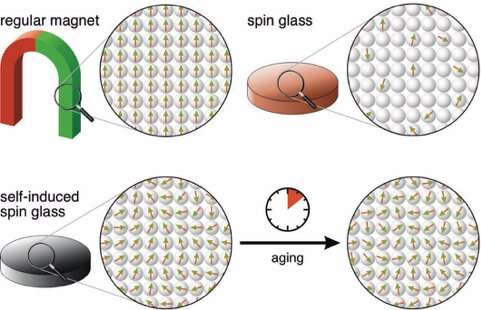
Contrary to regular magnets, spin glasses have randomly placed atomic magnets that point in all kinds of directions. Self-induced spin glasses are made of whirling magnets circulating at different speeds and constantly evolving over time. Credit: Daniel Wegner
The strongest permanent magnets today contain a mix of the elements neodymium and iron. However, neodymium on its own does not behave like any known magnet, confounding researchers for more than a half-century. Physicists at Radboud University and Uppsala University have shown that neodymium behaves like a self-induced spin glass, meaning that it is composed of a rippled sea of many tiny whirling magnets circulating at different speeds and constantly evolving over time. Understanding this new type of magnetic behaviour refines our understanding of elements on the periodic table, and could eventually pave the way for new materials for artificial intelligence. The results will be published on 29th of May, in Science.
"In a jar of honey, you may think that the once clear areas that turned milky yellow have gone bad. But rather, the jar of honey starts to crystallize. That's how you could perceive the 'ging process in neodymium," says Alexander Khajetoorians, professor in scanning probe microscopy. With professor Mikhail Katsnelson and assistant professor Daniel Wegner, he found that the material neodymium behaves in a complex magnetic way never before observed in an element on the periodic table.
Whirling magnets and glasses
Magnets are defined by a north and south pole. Dissecting a regular fridge magnet reveals many atomic magnets, so-called spins, that are aligned along the same direction and define the north and south pole. Quite differently, some alloy materials exist as a spin glass, in which randomly spaced spins point in all kinds of directions. Spin glasses derive their name from the amorphous, evolving structure of the atoms in a piece of glass. In this way, spin glasses link magnetic behaviour to phenomena in softer matter, like liquids and gels.
Spin glasses have been known to occur in alloys, which are combinations of metals with one or more other elements and with an amorphous structure, but never in pure elements of the periodic table. Surprisingly, Radboud researchers found that the atomic spins of a perfectly ordered piece of the rare-earth element neodymium form patterns that whirl like a helix but constantly change the exact pattern of the helix. This is the manifestation of a new state of matter called a self-induced spin glass.
Seeing the magnetic structure
"In Nijmegen, we are specialists in scanning tunneling microscopy (STM). It allows us to see the structure of individual atoms, and we can resolve the north and south poles of the atoms," Wegner explains. "With this advance in high-precision imaging, we were able to discover the behaviour in neodymium, because we could resolve the incredibly small changes in the magnetic structure. That's not an easy thing to do."
A material that behaves like neurons
This finding opens up the possibility that this complex and glassy magnetic behaviour could also be observed in new materials, including other elements on the periodic table. Khajetoorians says, "It will refine textbook knowledge of the basic properties of matter. But it will also provide a proving ground to develop new theories where we can link physics to other fields, for example, theoretical neuroscience. The complex evolution of neodymium may be a platform to mimic basic behaviour used in artificial intelligence. All the complex patterns which can be stored in this material can be linked to image recognition."
With the advancement of AI and its large energy footprint, there is increasing demand to create materials that can perform brain-like tasks directly in hardware. "You could never build a brain-inspired computer with simple magnets, but materials with this complex behaviour could be suitable candidates," Khajetoorians says.
More information: "Self-induced spin glass state in elemental eand crystalline neodymium" Science, science.sciencemag.org/cgi/doi … 1126/science.aay6757
Journal information: Science
Provided by Radboud University Nijmegen