Study demonstrates dogs promote page turning
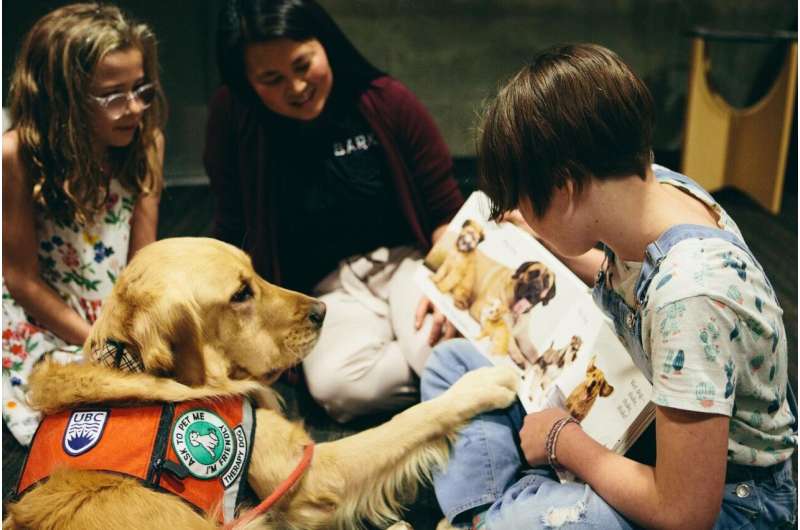

Reading in the presence of a pooch may be the page-turning motivation young children need, suggests a UBC researcher.
Camille Rousseau, a doctoral student in UBC Okanagan's School of Education, recently completed a study examining the behaviour of 17 children from Grades 1 to 3 while reading with and without a dog. The study was conducted with Christine Tardif-Williams, a professor at Brock University's department of child and youth studies.
"Our study focused on whether a child would be motivated to continue reading longer and persevere through moderately challenging passages when they are accompanied by a dog," explains Rousseau.
Participants were recruited based on their ability to read independently. Prior to the study, each child was tested to determine their reading range and to ensure they would be assigned appropriate story excerpts. The researchers then choose stories slightly beyond the child's reading level.
During the study's sessions, participants would read aloud to either an observer, the dog handler and their pet or without the dog. After finishing their first page, they would be offered the option of a second reading task or finishing the session.
"The findings showed that children spent significantly more time reading and showed more persistence when a dog—regardless of breed or age—was in the room as opposed to when they read without them," says Rousseau. "In addition, the children reported feeling more interested and more competent."
With the recent rise in popularity of therapy dog reading programs in schools, libraries and community organizations, Rousseau says their research could help to develop 'gold-standard' canine-assisted intervention strategies for struggling young readers.
"There have been studies that looked at the impact of therapy dogs on enhancing students' reading abilities, but this was the first study that carefully selected and assigned challenging reading to children," she says.
Some studies and programs have children choose their own book, and while the reading experience would still be positive, Rousseau adds it's the educational experience of persevering through a moderate challenge that offers a potentially greater sense of achievement.
She hopes the study increases organizations' understanding of how children's reading could be enhanced by furry friends.
More information: Camille Xinmei Rousseau et al, Turning the Page for Spot: The Potential of Therapy Dogs to Support Reading Motivation Among Young Children, Anthrozoös (2019). DOI: 10.1080/08927936.2019.1645511
Provided by University of British Columbia