Credit: RUDN University
A chemist from RUDN University has developed a catalyst for the production of eugenol acetate, a substance that destroys the larvae of mosquitoes transmitting dangerous diseases. The article was published in the journal Materials.
Aedes aegypti mosquitoes (yellow fever mosquitos) can carry Zika virus, yellow fever, chikungunya and dengue fever. Up to 20 percent of patients with yellow fever die, although there is a vaccine. There is no cure or vaccine for Zika virus or dengue fever. Therefore, the destruction of carriers is the only effective method of combating the spread of diseases. It is easier to kill mosquitoes at the larval stage, so an effective and affordable anti-larva drug, such as eugenol acetate, can seriously help humanity. Eugenol is the main component in the acetylation reaction, obtained from clove oil. However, it is not easy to synthesize pure eugenol acetate without impurities and with a high content of the target product (up to 90 percent). This is because catalysts suitable for such synthesis have not been created yet, and there are no non-catalytic methods for producing eugenol acetate. The yield of eugenol acetate in the reactions used in industry is only 20 to 30 percent.
RUDN chemist Rafael Luque has developed a new catalyst for eugenol acetylation to solve this problem. The chemists ensured that the catalyst can be removed from the reaction zone and reused. In addition, the temperature and reaction time are low while the yield of the target product is high.
At the first stage, the chemists analyzed the drawbacks of existing methods for the synthesis of eugenol acetate. Homogeneous catalysis with mineral acids can be used to acetylate eugenol. But this method does not allow simply separating the catalyst from the reaction products. With homogeneous catalysis, partial dissolution of the reactor in acid is also possible, which leads to contamination of the solution. Another method is based on the use of biocatalysts. They make it possible to obtain a yield of more than 90 percent of eugenol acetate and are environmentally friendly. However, the synthesis of biocatalysts is laborious and expensive, and the reuse of such catalysts is almost impossible. This makes the use of biocatalysts too expensive.
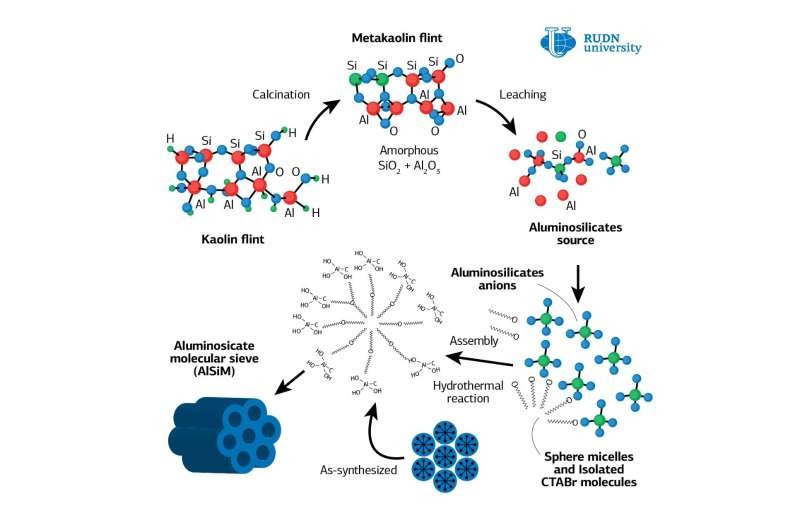
The RUDN chemists proposed creating a heterogeneous catalyst, where the active substance, heteropoly acid, is applied to a neutral solid carrier. Heteropoly acids are derivatives of oxygen acids in which oxygen ions are completely or partially replaced by acid residues of other acids. Heteropoly acids have a greater catalytic activity than mineral acids, and, unlike mineral acids, they do not produce adverse reactions that pollute the solution. The chemists have suggested that heterogeneous catalysts, consisting of several components, may be the optimal solution, since the solid catalyst and the substance in solution are in different phases, and it is not difficult to separate them.
For a heterogeneous catalyst synthesis, the chemists applied a heteropoly acid to a solid carrier—mesoporous aluminosilicate (AlSiM). This is a highly porous substance with a large surface area (up to 1000 m2/g) and cylindrical pores of the same size. For its production, TEOS (tetraethoxysilane), a toxic and expensive component, is most often used as a source of silicon. Rafael Luque and his colleagues showed that instead of TEOS, you can use silicon-rich natural kaolin, which usually goes to waste in the development of deposits. The use of kaolin to obtain AlSiM will significantly reduce the cost of production of the catalyst carrier and reduce the negative environmental impact.
The new catalyst is easily removed from the reaction zone and retains its activity even after several repeated cycles, allows the reaction to be carried out quickly and without impurities, has high stability and relatively low cost compared to biocatalysts. The product yield amounted to 99.9 percent. With repeated cycles, the yield changes slightly and even after the fifth cycle it comes out at 90 percent. The catalyst can be recommended for the industrial production of eugenol acetate.
More information: Alex de Nazaré de Oliveira et al. Acetylation of Eugenol over 12-Molybdophosphoric Acid Anchored in Mesoporous Silicate Support Synthesized from Flint Kaolin, Materials (2019). DOI: 10.3390/ma12182995
Provided by RUDN University