Discovery of plant immune signaling intermediary could lead to more pest-resistant crops

A new actor in the immune system of plants has been identified. KAUST scientists have identified the protein MAP4K4 is needed to mount proper defenses against environmental pathogens.
The discovery helps explain the tight control of immune signaling in plants and reveals targets in a molecular pathway that could be manipulated by crop breeders. "Our findings are directly applicable to make plants more resistant to pathogens," says study author, Heribert Hirt, professor of plant science at KAUST's Center for Desert Agriculture.
MAP4K4 (short for mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4) is a well-established player in human immunity and inflammation, but its role in plant disease resistance was unknown. Hirt and his collaborators stumbled on it during a large screen for proteins involved in signal transduction in the weedy thale cress Arabidopsis. By studying mutant plants that lack a working copy of MAP4K4, Hirt's team then drilled down into the core functions of this protein.
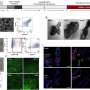
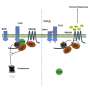
First, they showed that MAP4K4 was essential for proper immune responses to flg22, a peptide derived from a bacterial protein found within the filamentous flagellum of disease-causing microbes. Working with colleagues in France, the KAUST researchers—led by Hirt and postdoctoral fellow, Yunhe Jiang—then detailed how.
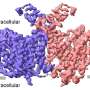
They demonstrated that MAP4K4 directly adds chemical tags (in the form of phosphate groups) at several sites of another protein, BIK1. This helps stabilize BIK1 and promotes the production of highly toxic molecules that play a central role in pathogen resistance, explains Jiang. The researchers also showed that MAP4K4 tags a repressor of BIK1 with phosphate decorations. This chemical adornment disables the negative regulator to further promote BIK1 activation.
So far, Hirt and his group have only described this function of MAP4K4 in Arabidopsis immunity. They reported the findings in EMBO Reports.
"The next step is to test our findings also in crops by generating knock-out mutants," Hirt says. "This is quite feasible now by using CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing technology that is established in tomato, rice and other species of agricultural importance."

The researchers also plan to examine the roles of other regulatory proteins within the MAP4K family, of which at least 10 exist in plants. Intriguingly, Jiang showed that one family member, MAP4K3, seems to act synergistically with MAP4K4 to control BIK1 stabilization and pathogen-induced immune responses.
Closely related MAP4K proteins may thus share overlapping functions but also have distinct features that collectively contribute to the fidelity of immune signaling in plants. A better knowledge of these signaling mechanisms could help agribusinesses keep plant pathogens at bay.
More information: Yunhe Jiang et al. MAP 4K4 associates with BIK 1 to regulate plant innate immunity, EMBO reports (2019). DOI: 10.15252/embr.201947965
Journal information: EMBO Reports