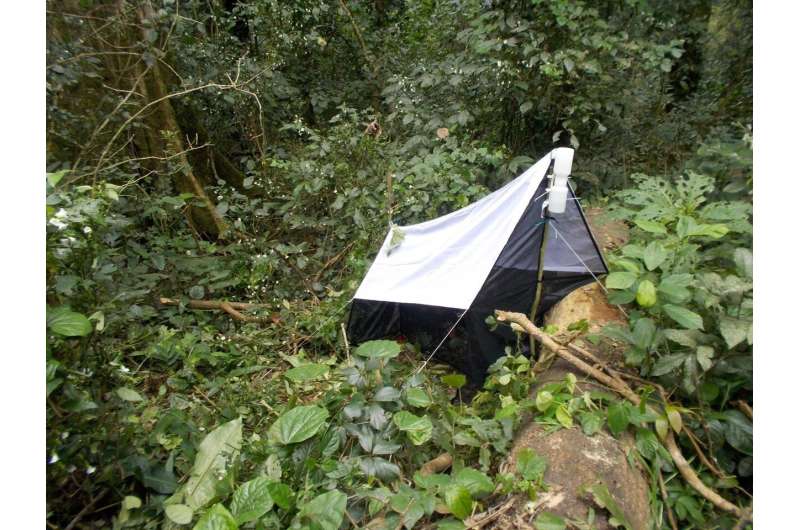
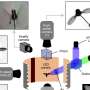
The wasps were collected with tent-like Malaise traps. Credit: Tapani Hopkins
Scientists at the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku in Finland have studied the diversity of tropical parasitoid wasps for years. Parasitoid wasps are among the most species rich animal taxa on Earth, but their tropical diversity is still poorly known. Recently, the research group sampled Afrotropical rhyssine wasps, which are among the largest wasps. Scientists from three countries and research institutes participated in the research led by the University of Turku research group.
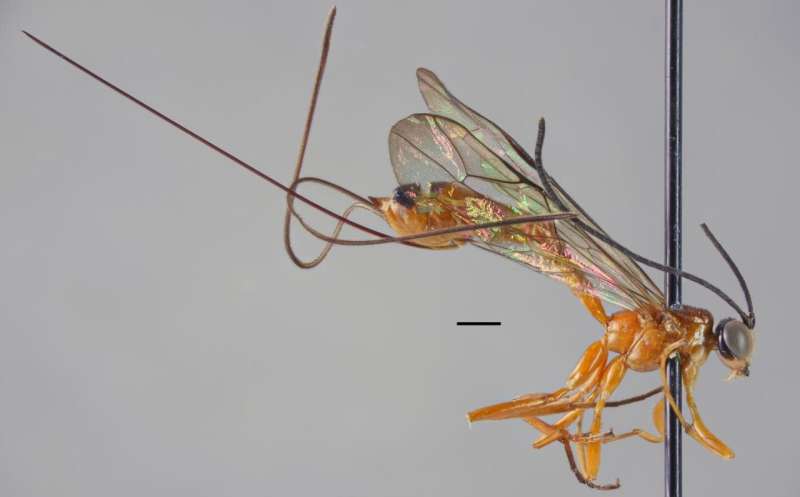
Rhyssines are sizeable wasps that parasitise the beetle or wasp larvae of decaying wood. The largest species can grow over ten centimetres in length. Females carry an extremely long ovipositor, which is used to drill through wood, stab and paralyse the host, and lay eggs.
Large-sized insect species are usually known better than small species, but tropical rhyssines are an exception.
"A good example of how poorly tropical rhyssines are known is the species Epirhyssa overlaeti, which is the largest African rhyssine. Only two females were known before, one collected in the 1930s in the Congo and the other one in Cameroon in the 1980s. Now, at one single Ugandan site, we found large numbers of both females and males. This completely changed what is known of the distribution of the species," says Doctoral Candidate Tapani Hopkins from the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku, who led the project.
Scientists at the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku have previously studied the diversity of rhyssine wasps especially in the Amazonian lowland rainforest.
-
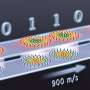
Epirhyssa johanna, a species new to science from Uganda. Credit: from the publication Hopkins et al. 2019
-
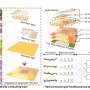
Epirhyssa quagga, a species new to science from Uganda. Photo from the publication Hopkins et al. 2019. Credit: from the publication Hopkins et al. 2019
"In our Amazonian research, we have described ten large-sized South-American species new to science and our understanding of the diversity of South American tropical rainforest parasitoid wasps has changed. Extending the research to the African continent is important, because our goal is to understand the global diversity of the parasitoid insects which are extremely species rich," says Professor in Biodiversity Research Ilari Sääksjärvi from the Biodiversity Unit of the University of Turku.
In the newest study, two new African tropical parasitoid wasp species were described.
"We named one of the new species Epirhyssa quagga, because its colouration resembles that of a zebra. The other species became Epirhyssa johanna. The name Johanna refers to my wife," Hopkins says delightedly.
More information: Tapani Hopkins et al, Extensive sampling and thorough taxonomic assessment of Afrotropical Rhyssinae (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonidae) reveals two new species and demonstrates the limitations of previous sampling efforts, ZooKeys (2019). DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.878.37845
Journal information: ZooKeys
Provided by University of Turku