Indonesia under 'blanket of smoke' amid wildfires
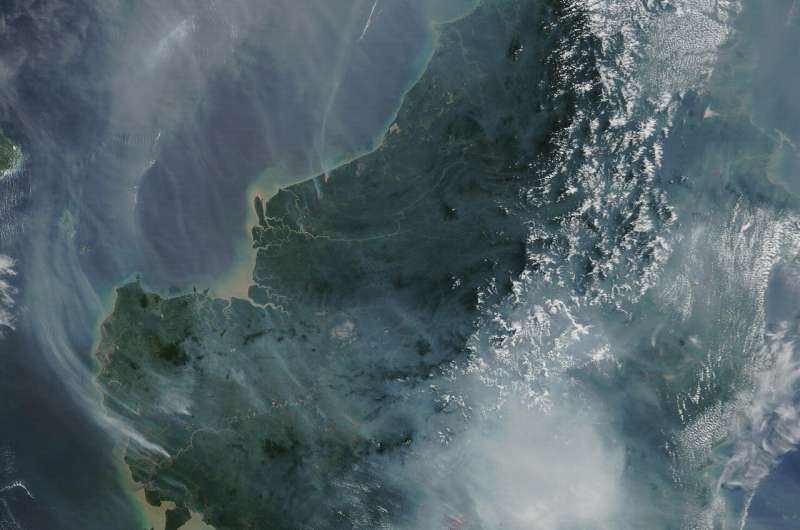

Indonesia is under a "blanket of smoke" amid wildfires that threaten humans, wildlife and the global climate, researchers say.
The wildfires—some started by "slash-and-burn" methods for turning forests into farmland—happen yearly in Indonesia, but 2019's fire season has been particularly damaging, with more than 320,000 hectares (twice the size of Greater London) burned already.
University of Exeter researcher Abi Gwynn, who is in the country to study how previous fires have affected orangutans, says smoke has obscured the sky over Palangka Raya in Central Kalimantan (Indonesian Borneo) for two months.
She says hospitals are full of people in need of oxygen, and she warns that the fires are destroying precious wildlife habitats and peatland that stores vast quantities of carbon.
"Indonesia has been in a state of emergency for two months now and we have been living under a blanket of smoke," said Gwynn, a masters by research student at Exeter's Penryn Campus in Cornwall.
"I can smell the smoke constantly and always have to wear a mask when going outside.
"This fire season, Palangka Raya has been a very unhealthy place to be. We've experienced an air quality index of over 2,000 – anything over 150 is considered unhealthy.
"Many local people don't wear masks and carry on as usual. Schools were shut for about two weeks but have now reopened, as the air quality has improved a little over the last few days."
Gwynn's fieldwork is currently on hold because her partner organization, Borneo Nature Foundation, has suspended all non-essential forest work to protect staff health and to allow efforts to be focused on firefighting.
Wildfires are also burning in other countries, including Brazil, but Gwynn says Indonesia is a concerning case due to the "kindling beneath the flames."
"Asia contains approximately 38% of the world's tropical peatlands, with Indonesia being the major contributor. Much of these naturally flooded peatlands have been drained for agriculture, or drained by the construction of canals to export timber from forests. These now drier peat soils are highly flammable, burning below ground as well as above which makes fires extremely difficult to extinguish," she said.
"Most people know the importance of tropical rainforests such as the Amazon in providing oxygen and storing carbon, but peatland soils are the unsung heroes of climate regulation.
"Covering just 3% of the Earth's land surface, peatlands store between 32-46% of the world's soil carbon pool.
"Despite their importance, Indonesian peatlands are currently one of the most exploited ecosystems on Earth."
Indonesia's peat swamp forests also contain hundreds of species of plants, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians and freshwater fish.
"Many of these species are already highly threatened and spiraling towards extinction," Gwynn said.
"Every year, forest fires consume more and more vital habitat animals rely on to survive.
"Some slower-moving animals such as turtles, snakes and frogs are unable to escape the flames and burn alive.
"Others, including the birds and mammals, may escape the immediate danger but subsequently suffer from starvation and respiratory diseases caused by the smoke."
"The question of 'who started the fire' is complex. Small scale land clearance by fire can be sustainable in the long-term provided peatlands are undrained, in their natural flooded state. Problems tend to occur when people burn their land, whether this be local people or industrial oil palm/Acacia plantations, in areas which have been drained and thus the land is much more prone to burning indefinitely until the rains come." said Dr. Alex Thornton, of the University of Exeter.
"There is no quick fix to this issue in Indonesia. There are a host of political, social and economic challenges to be solved."
"Long-term solutions must come from better law enforcement to ensure land clearance in responsible and restoration of drained peatlands to prevent future fires."
More information: Thomas Gumbricht et al. An expert system model for mapping tropical wetlands and peatlands reveals South America as the largest contributor, Global Change Biology (2017). DOI: 10.1111/gcb.13689
Journal information: Global Change Biology
Provided by University of Exeter