Metabolic engineering method succeeds in producing 1,2,4-butanetriol sustainably from biomass
A more environmentally-friendly and sustainable method of producing the useful chemical 1,2,4-butanetriol has been discovered. The Kobe University team were the first in the world to utilize a method involving the direct fermentation of xylose in rice straw using an engineered yeast strain to produce 1,2,4-butanetriol. In the course of conducting this research, the team successfully overcame two bottlenecks to maximize the production.
The research was conducted by Academic Researcher Takahiro Bamba and Professor Akihiko Kondo (from the Graduate School of Science, Technology and Innovation), and Professor Tomohisa Hasunuma (of the Engineering Biology Research Center).
1,2,4-butanetriol uses and current production methods:
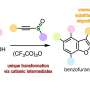
The commodity chemical 1,2,4-butanetriol has a wide variety of practical uses across different fields. For example, it can be utilized in the production of solvents and to synthesize various pharmaceutical products—such as anti-viral and cholesterol-lowering drugs, among others.
Current methods of producing 1,2,4-butanetriol use raw materials derived from oil and result in byproducts that are harmful to the environment. The most common way to produce the chemical is by using sodium borohydride (NaBH4) to chemically reduce malic acid to 1,2,4-butanetriol. However the process generates a large amount of borate salts. Disposing of these salts causes pollution. Chromite and rubidium can also be used as catalysts for 1,2,4-butanetriol production, however these methods require high temperature and high pressure, and also result in toxic byproducts.
Deriving xylose (the second most abundant natural sugar) from lignocellulosic biomass (dry plant matter) and using it to produce chemicals offers multiple advantages as it is a renewable resource that causes far less environmental pollution. It provides a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based production.
Methodology
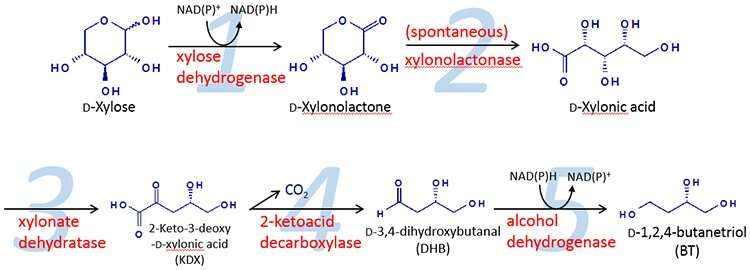
As shown in Figure 1, 1,2,4-butanetriol is produced by microbes through a 5 stage reaction process within the cells.
However in steps 1, 3 and 4 of the reaction, there were no enzymes to provide a catalyst in the yeast. In this study, rice straw hydrolysate was used to produce xylose. The yeast used was genetically engineered with the required enzymes in order to successfully produce an efficient yield of 1,2,4-butanetriol.
In the first successful trial, only 0.02g/L of 1,2,4-butanetriol was produced. By examining these results, it became apparent that there were insufficient catalytic activities for stage 3 and stage 4 inside the yeast cells. This meant that the reaction was slowed down in stages 3 and 4. These reactions were considered to be bottlenecks.

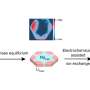
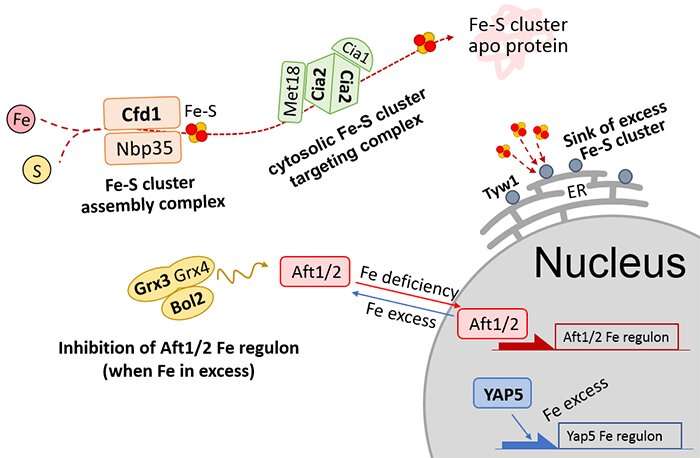
With the presence of iron sulphur clusters within the structure of the xylonate dehydratase catalyst in stage 3, it became clear that it was difficult for the yeast to maintain a reaction with the iron sulphur protein in the cells. This was due to an insufficient amount of iron sulphur clusters within the yeast cells.
Iron (Fe) is essential for the yeast cells to produce 1,2,4-butanetriol, however too much iron damages the cells. Metabolic engineering (optimizing regulatory and genetic processes within cells to increase the production of a particular substance) was utilized to further genetically modify the yeast in order to increase its iron metabolism. This improved the yeast's reactivity with the xylonate dehydratase and ensured that functional Fe-S enzymes were formed (Figure 2). Using this modified yeast strain improved catalytic activity by approximately 6 times.
Furthermore, the stage 4 bottleneck was overcome by using KdcA (derived from Lactococcus lactis- a bacterium commonly used for fermentation in the food industry) as the decarboxylase to provide sufficient catalytic activity.
Results
Ultimately, this method succeeded in producing 1.7g/L of 1,2,4-butanetriol when engineered yeast was used. In addition, 1.1 g/L of 1,2,4-butanetriol was produced by the rice straw hydrolysate solution that was used as the medium during the fermentation experiment (Figure 3).
This research suggests that it would be possible to produce other chemicals that require iron sulphur proteins using a similar method. Optimizing the metabolic pathway in this study through further research would allow for greater production of useful compounds from lignocellulosic biomass. This could potentially reduce future dependence on finite oil resources and polluting methods of production.
More information: Takahiro Bamba et al, Production of 1,2,4-butanetriol from xylose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae through Fe metabolic engineering, Metabolic Engineering (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2019.08.012
Provided by Kobe University