Scientists find longevity biomarkers
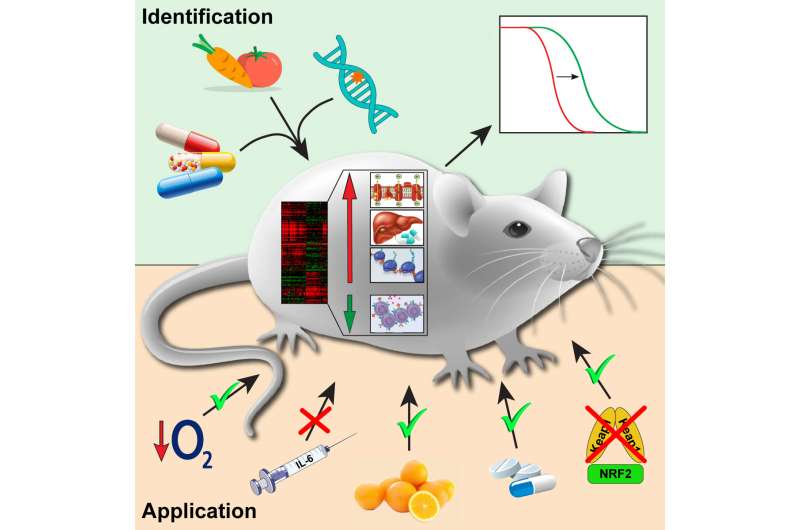
An international group of scientists studied the effects of 17 lifespan-extending interventions on gene activity in mice and discovered genetic biomarkers of longevity. The results of their study were published in the journal Cell Metabolism.
Nowadays, dozens of interventions are known that extend the lifespan of various living organisms ranging from yeast to mammals. They include chemical compounds (e.g. rapamycin), genetic interventions (e.g. mutations associated with disruption of growth hormone synthesis), and diets (e.g. caloric restriction). Some targets of these interventions have been discovered. However, there is still no clear understanding of the systemic molecular mechanisms leading to lifespan extension.
A group of scientists from Skoltech, Moscow State University and Harvard University decided to fill this gap and identify crucial molecular processes associated with longevity. To do so, they looked at the effects of various lifespan-extending interventions on the activity of genes in a mouse, a commonly used model organism closely related to humans.
The scientists identified a group of genes, whose activity was associated with longevity in response to various interventions, serving as biomarkers of lifespan extension.
"In our lab, we subjected mice of different sexes and ages to 8 longevity interventions and analyzed gene expression changes induced by these treatments. After aggregating our data with the datasets published by other groups, we obtained the gene activity profiles of 17 interventions. Although in general the effects produced by individual treatments turned out to be quite specific, a certain group of genes changed its expression in a similar way in response to different lifespan-extending interventions," says the first author of the study, Alexander Tyshkovskiy.
The scientists then applied the discovered biomarkers to search for other interventions with the same effect on their activity and, therefore, a high potential for lifespan extension. In their work, the researchers identified several such treatments, including chronic hypoxia and chemical compounds, such as the antioxidant ascorbyl palmitate and the mTOR inhibitor, KU-0063794.
"Currently, we are validating these hits by testing their effect on the lifespan of mice. We hope that our biomarkers will significantly facilitate the search for new longevity interventions and help improve the health-span and lifespan in rodents and, in the long term, in humans," says Alexander.
In addition to their scientific research, the scientists developed GENtervention, an application that offers fast and user-friendly tools for investigating the associations between the activity of individual genes and longevity.
More information: Alexander Tyshkovskiy et al. Identification and Application of Gene Expression Signatures Associated with Lifespan Extension, Cell Metabolism (2019). DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.018
Journal information: Cell Metabolism
Provided by Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology