Scientists develop stereodefined N and S atom-codoped graphdiyne for oxygen evolution
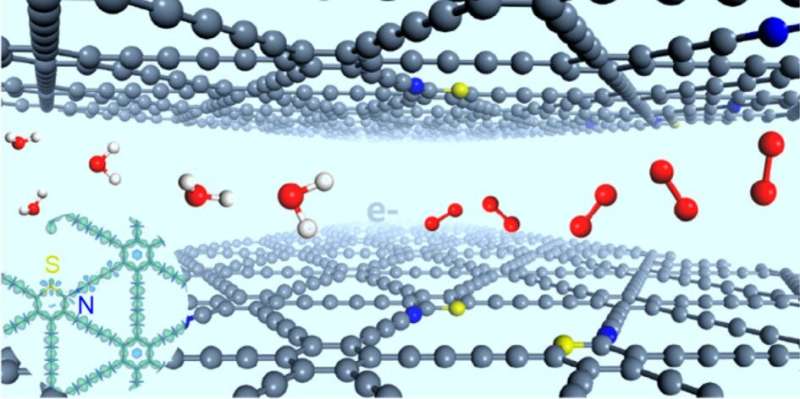
The oxygen evolution reaction (OER) is of great significance in energy-related techniques such as metal-air batteries and water splitting. Chinese scientists have doped site-defined sp-N and S atoms into graphdiyne, which enables highly active catalysis of OER. Their findings were published in J. Am. Chem. Soc.
Traditional OER catalysts, e.g. RuO2 and IrO2, are limited by high cost and declining stability. Heteroatom-doped carbon materials, especially dual doping, have displayed intriguing potential for highly efficient electrocatalysis owing to the synergistic effect. However, the doping sites for different atoms are highly uncontrollable, which makes the structure-property study difficult.
The synergistic effect can only take place within a certain distance between the dual atoms, and 7.5 Å is the upper limit for N and S atoms to obtain a strong synergistic effect.
Scientists from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences successfully prepared "stereodefined" N and S atoms codoped graphdiyne, and the relative positions of the N and S atoms were well controlled.
"N-, S-codoped graphdiyne presented higher catalytic activity than those catalysts with individual-element doping (N or S atom) and commercial RuO2 in catalyzing the OER, possessing lower overpotential (299 mV) and higher current density (47.2 mA/cm2, 1.6 V), " said WANG Dan, who led this research.
This study opens an avenue for understanding the synergistic effects in heteroelement-doped metal-free catalysts, and for further guiding the rational design and preparation of highly efficient catalysts for energy conversion and storage.
-
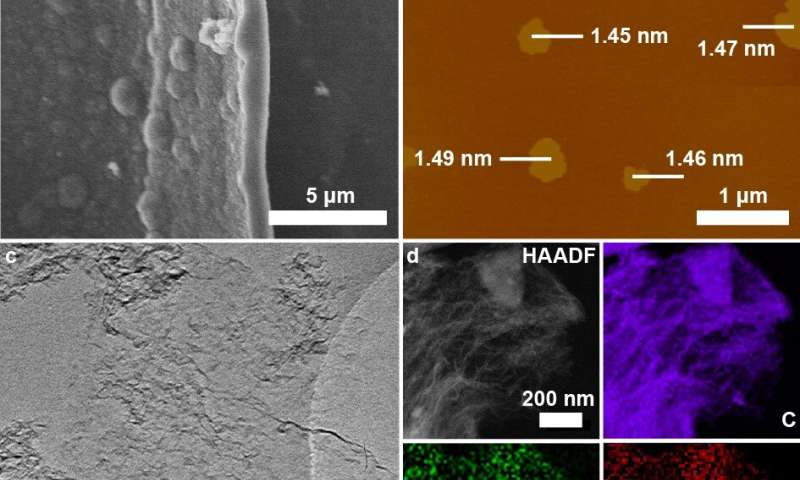
SEM, AFM and TEM characterizations of catalysts. Credit: Zhao Yasong -
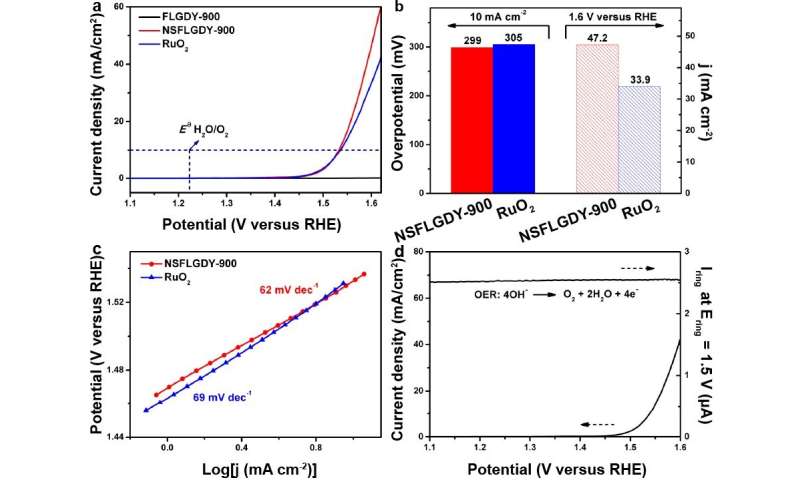
OER performance of catalysts and commercial RuO2. Credit: Zhao Yasong
More information: Yasong Zhao et al, Stereodefined Codoping of sp-N and S Atoms in Few-Layer Graphdiyne for Oxygen Evolution Reaction, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2019). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b13695
Journal information: Journal of the American Chemical Society
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences