Credit: CC0 Public Domain
Hydrogenases are enzymes that catalyze hydrogen activation. There are three types of hydrogenases in nature, all containing iron and some of them nickel. But in synthetic chemistry there is a whole host of metals that can activate molecular hydrogen and catalyze hydrogenation reactions.
"Why doesn't nature use other metals in hydrogenases? Is it purely due to bioavailability?" asks Xile Hu, head of the Laboratory of Inorganic Synthesis and Catalysis at EPFL. The answer is probably not simple, since metalloenzymes containing molybdenum, manganese, cobalt, and copper are pretty common.
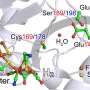
Working with the lab of Seigo Shima at the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology, Hu's lab has now synthesized a manganese-hydrogenase by incorporating a manganese complex into the apoenzyme (the active-site free part) of iron-hydrogenase.
"What is exciting is that this semi-synthetic manganese-hydrogenase is active for the native reaction of iron-hydrogenase," says Hu. This is important because, generally speaking, replacing native metals while maintaining the enzyme's activity is rare. "To our knowledge, this is the first functional non-native metal hydrogenase."
More information: Hui-Jie Pan et al. A catalytically active [Mn]-hydrogenase incorporating a non-native metal cofactor, Nature Chemistry (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41557-019-0266-1
Journal information: Nature Chemistry
Provided by Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne