Scientists identify novel function of self-renewal factor of spermatogonial stem cells
A research team reports a novel function of fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2), a self-renewal factor for spermatogonial stem cell (SSC) which is the origin of sperm production. Although it has demonstrated that both FGF2 and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is indispensable for SSC self-renewal and survival in vitro, the present study reveals that FGF2 has different properties from GDNF in mouse testis. This finding will contribute to the regulation of SSCs in vivo for the treatment of male infertility.
This study was published in Stem Cell Reports.
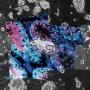
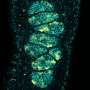
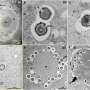
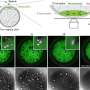
Dr. Seiji Takashima, an assistant professor of the Faculty of Textile Science and Technology in Shinshu University and the corresponding author on the paper, successfully identified a novel function of FGF2 in mouse testis using a biodegradable gelatin microsphere system capable of sustained diffusion of self-renewal factors for several days in vivo.
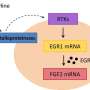
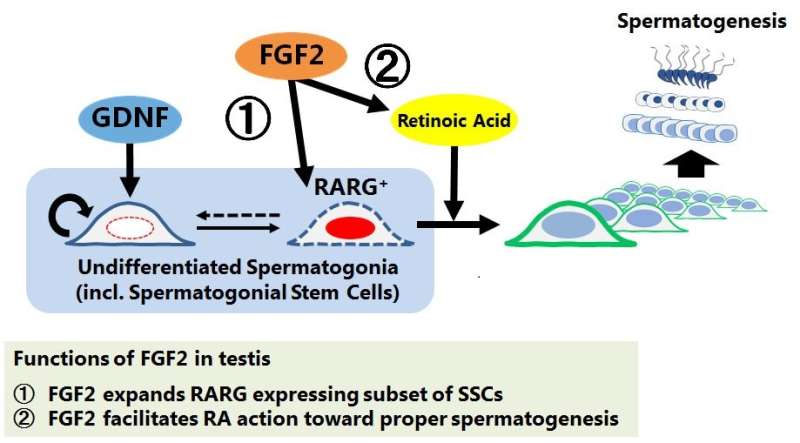
Consecutive production of sperm is ensured by the repeat of self-renewal and differentiation of SSCs. It was well known that the self-renewal of SSCs is promoted by GDNF, while retinoic acid (RA) induces the differentiation toward sperm production. In 2015, Dr. Takashima found that FGF2 (fibroblast growth factor 2) also act as a self-renewal factor for SSCs in vitro. In the present study, his group demonstrated that FGF2 conversely acts as a differentiation promoting factor in vivo.
They found that FGF2-stimulated SSCs frequently express a receptor for RA when compared to those stimulated by GDNF, suggesting that FGF2 expands differentiation-susceptible subset of SSCs. Simultaneously, they also demonstrated that this molecule acts on the testicular microenvironment, which is required for SSC function, to facilitate RA action. These results demonstrate that FGF2, which, in 2015, was shown to be bona fide self-renewal factor for SSCs in vitro, can conversely act to facilitate SSC differentiation in vivo. Considering that GDNF/FGF2 ratio shows dynamic change during testicular development and regeneration, the functional balance between GDNF and FGF2 might play a pivotal role in the regulation of sperm production from SSCs.
The finding will contribute not only to understanding the principle of sperm production but also to future applications for male infertility treatment, breeding live stock, and conservation of endangered species.
More information: Kaito Masaki et al, FGF2 Has Distinct Molecular Functions from GDNF in the Mouse Germline Niche, Stem Cell Reports (2018). DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.03.016
Journal information: Stem Cell Reports
Provided by Shinshu University