The physics of better batteries

Harvard University researchers are using physics to solve one of the biggest challenges in designing light-weight, long-lasting batteries: how to squeeze more energy into less space.
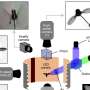
Researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and the Department of Physics have developed a tunable, electrochemical system that can store large amounts of energy in the space between atomically thin sheets of layered two-dimensional materials, like graphene.
The research is published in Nature.
"We observed that by stacking sheets of different, atomically thin materials, we could engineer higher electrochemical capacities, improving the accumulation of charge in the hybrid material by more than tenfold," said Kwabena Bediako, former postdoctoral fellow at SEAS and first author of the paper.
Bediako is currently an assistant professor of chemistry at University of California, Berkeley.
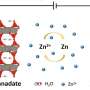
The researchers exploited a physical effect known as van der Waals forces, which are weak bonds between molecules based on the total number of atoms and proximity rather than direct chemical interactions. Traditional techniques for improving materials (making better electrodes in lithium-ion batteries, for instance) are limited to elements and compounds that are chemically and structurally compatible, such as cobalt and nickel. But, by bonding materials with van der Waals forces, the researchers found that they could combine any two layered materials to create a new electrochemical environment in the "empty" space between the two layers, known as the van der Waals interface.
The researchers stacked layers of boron nitride, graphene and molybdenum dichalcogenide (MoX2) and injected lithium ions between the layers. The graphene provided a low-resistance electronic pathway, which in turn enabled the layer of MoX2 to hold onto lithium ions more efficiently. These experimental observations were confirmed by detailed theoretical modeling of where the lithium atoms reside. The theoretical modeling also explains the mechanisms of insertion and removal of the lithium atoms, a crucial step in understanding the ability of the device to function as a rechargeable battery.
"At an atomic level, this electrochemical device is more than the sum of its parts," said Bediako. "We've created a unique electrochemical environment between these layers and we can measure, control and tune it to store more lithium ions over longer periods of time and at a desired voltage."
The more lithium ions you can squeeze into a space, the higher the capacity of the battery; the more readily the ions come out, the higher the voltage.
"Beyond energy storage, this method for manipulating and characterizing the electrochemical behavior of layered systems opens new pathways to control a large charge density in 2-D electronic and optoelectronic devices," said Philip Kim, professor of physics and of applied physics at SEAS and senior author of the paper.
More information: D. Kwabena Bediako et al. Heterointerface effects in the electrointercalation of van der Waals heterostructures, Nature (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0205-0
Journal information: Nature
Provided by Harvard University