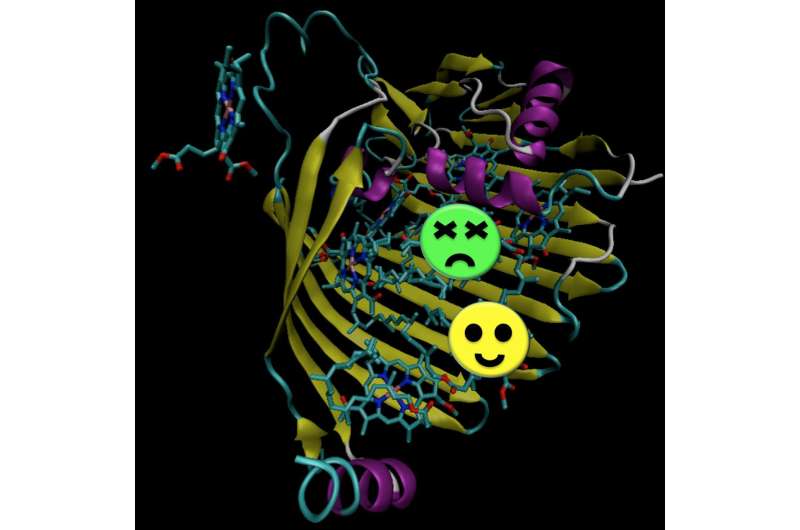
The figure shows the photosynthetic complex of light-harvesting green sulfur bacteria the green and yellow circles highlight the two molecules simultaneously excited. Credit: dr. Thomas la Cour Jansen/University of Groningen
Molecules that are involved in photosynthesis exhibit the same quantum effects as non-living matter, concludes an international team of scientists including University of Groningen theoretical physicist Thomas la Cour Jansen. This is the first time that quantum mechanical behavior was proven to exist in biological systems that are involved in photosynthesis. The interpretation of these quantum effects in photosynthesis may help in the development of nature-inspired light-harvesting devices. The results were published in Nature Chemistry on 21 May.
For several years now, there has been a debate about quantum effects in biological systems. The basic idea is that electrons in can be in two states at once, until they are observed. This may be compared to the thought experiment known as Schrödinger's Cat. The cat is locked in a box with a vial of a toxic substance. If the cap of the vial is locked with a quantum system, it may simultaneously be open or closed, so the cat is in a mixture of the states "dead" and "alive," until we open the box and observe the system. This is precisely the apparent behavior of electrons.
Vibrations
In earlier research, scientists had already found signals suggesting that light-harvesting molecules in bacteria may be excited into two states simultaneously. In itself this proved the involvement of quantum mechanical effects, however in those experiments, that excited state supposedly lasted more than 1 picosecond (0.000 000 000 001 second). This is much longer than one would expect on the basis of quantum mechanical theory.
Jansen and his colleagues show in their publication that this earlier observation is wrong. "We have shown that the quantum effects they reported were simply regular vibrations of the molecules." Therefore, the team continued the search. "We wondered if we might be able to observe that Schrödinger cat situation."
Superposition
They used different polarizations of light to perform measurements in light-harvesting green sulfur bacteria. The bacteria have a photosynthetic complex, made up of seven light sensitive molecules. A photon will excite two of those molecules, but the energy is superimposed on both. So just like the cat is dead or alive, one or the other molecule is excited by the photon. "In the case of such a superposition, spectroscopy should show a specific oscillating signal," explains Jansen. "And that is indeed what we saw. Furthermore, we found quantum effects that lasted precisely as long as one would expect based on theory and proved that these belong to energy superimposed on two molecules simultaneously." Jansen concludes that biological systems exhibit the same quantum effects as non-biological systems.
The observation techniques developed for this research project may be applied to different systems, both biological and non-biological. Jansen is happy with the results. "This is an interesting observation for anyone who is interested in the fascinating world of quantum mechanics. Moreover, the results may play a role in the development of new systems, such as the storage of solar energy or the development of quantum computers."
More information: Erling Thyrhaug et al, Identification and characterization of diverse coherences in the Fenna–Matthews–Olson complex, Nature Chemistry (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s41557-018-0060-5
Journal information: Nature Chemistry
Provided by University of Groningen