Physicists at Saarland University in Saarbrücken, Germany, have succeeded in entangling a single atom with a single photon in the telecom wavelength range. This constitutes a basic building block for transmission of quantum information over long distance with low loss. The results have raised interest in the quantum technology community and are now published in Nature Communications.
Communication using quantum states offers ultimate security, because eavesdropping attempts perturb the signal and would therefore not remain undetected. For the same reason, though, long-distance transmission of that information is difficult. In classical telecommunication, the increasing attenuation of the signal is counteracted by measuring, amplifying and re-sending it in so-called repeater stations, but this turns out to be as detrimental to the quantum information as an eavesdropper.
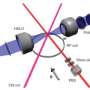
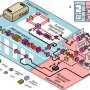
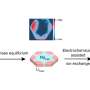
Therefore, a different principle has to be used: the quantum repeater. Here, quantum entanglement is first established over short distance and then propagated to longer separations. Quantum entanglement between two particles means that their common state is precisely defined, although when one measures the individual states of the particles, the results are random and unpredictable. A possible realization is to entangle a single atom with a photon that it emits. This is what happens in the laboratories of Prof. Jürgen Eschner, employing single calcium atoms in an ion trap that are controlled by laser pulses (www.uni-saarland.de/en/lehrstuhl/eschner.html). For the wavelength of 854 nanometers where atom-photon entanglement is created, however, no low-loss optical fibers for long-distance transmission exist; instead, one would like to transmit the photons in one of the so-called telecom bands (1300 – 1560 nanometers). The technology for converting the photons into this regime, the quantum frequency converter, has been developed by Prof. Christoph Becher and his research group (www.uni-saarland.de/fak7/becher/index.htm).
Together, the two groups have now demonstrated that after quantum frequency conversion, the telecom photon is still entangled with the atom that emitted the original photon, and that the high quality of the entanglement is maintained. One of the fascinating aspects of the work is that the entangled quantum state of the two microscopic particles (a single atom and a single telecom photon) extends over several floors of the physics building of the university. "This paves the way for entanglement over 20 kilometers and more", comments Matthias Bock, Ph.D. student in quantum technologies and first author of the study. The results are an important step towards integrating quantum technologies into conventional telecommunications; for their research towards this goal, the two groups at Saarland University are funded by the German Ministry for Education and Research, BMBF.
Explanation of quantum entanglement:
The state of an individual quantum bit (an atom with two energy states of its electron, or a photon with two directions of its polarization) may be visualized as a point on the surface of a sphere. Measurement of that state provides an unpredictable result anywhere on the surface. The other qubit that is entangled with the first one will, however, always be found in the opposite point on the sphere. This correlation may also exist over large distances. Einstein called this phenomenon "spooky action at a distance"; it belongs to the non-intuitive peculiarities of quantum mechanics, but it has been confirmed in many experiments.
More information: Matthias Bock et al. High-fidelity entanglement between a trapped ion and a telecom photon via quantum frequency conversion, Nature Communications (2018). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04341-2
Journal information: Nature Communications
Provided by Saarland University