What do animals want? Team unpacks behavioral strategies using machine learning
Scientists have developed a new approach to understanding animal preferences, and the findings could provide greater insight into decision-making in humans.
Pet owners are familiar with the challenges of figuring out what their pets want. Building on Pavlov's work teaching his dogs to associate the ringing of a bell with food, researchers have tried to understand how animals and humans react to rewards under different circumstances. However, in the real world, what constitutes a reward and how this may motivate behavior are rarely clear.
Writing in PLOS Computational Biology, a team of scientists at Kyoto University's Graduate School of Biostudies report how worms evaluate a potential reward, examining their reactions by studying their movements.
"Current behavioral models are based on known rewards, so we can't use them to study freely behaving animals," explains lead author Shoichiro Yamaguchi. "We realized that we needed to look at the inverse case, and more accurately define the value of rewards from the behavior of the organism."
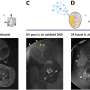
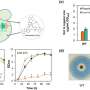
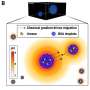
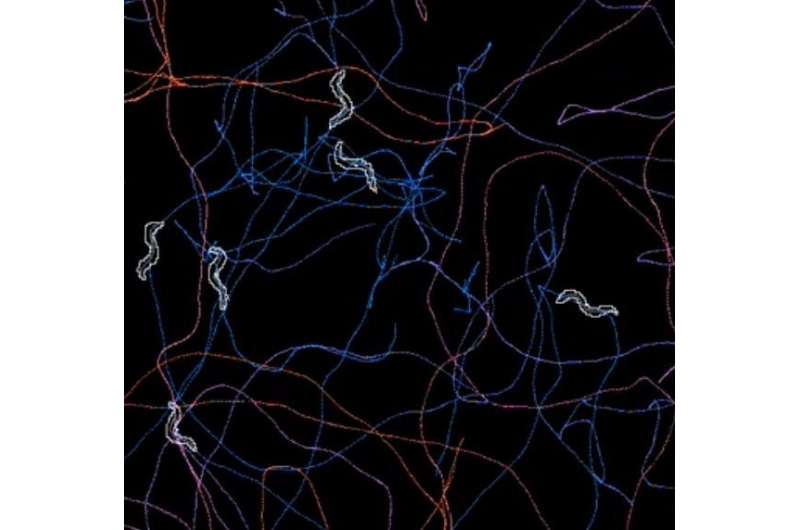
The team observed heat-sensitive worms as they searched for food on surfaces with different temperature zones, applying a machine learning method to understand how potential food rewards guided the movements.
Worms initially fed at a certain temperature were then observed to move toward that temperature zone when transferred to a plate with a range of different surface temperatures. In contrast, worms that were starved at a certain temperature, and then transferred, moved away from that zone.
The team's model showed that the fed worms sensed not only the environmental temperature, but also the change of temperature as they moved over different zones. The worms combined these sensations into a behavioral strategy to reach food using a minimal amount of energy, comparable to rational decision-making in humans.
Interestingly, the starved worms based their movements only on the temperature of the environment to escape from temperature zones they considered unlikely to contain food.
"Our approach accurately reproduces this simple worm behavior and gives much deeper insights into its underlying mechanism," elaborates senior scientist Honda Naoki. "Combining our approach with neurological measurements of freely behaving animals could help us better understand the essence of decision-making in higher animals as well as guide developments in artificial intelligence."
More information: Shoichiro Yamaguchi et al, Identification of animal behavioral strategies by inverse reinforcement learning, PLOS Computational Biology (2018). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006122
Journal information: PLoS Computational Biology
Provided by Kyoto University