Artificial bio-inspired membranes for water filtration
Access to clean drinking water is considered to be one of the main challenges of the 21st Century, and scientists have just opened a path to new filtration processes. Inspired by cellular proteins, they have developed membranes with asymmetric artificial channels in the interior, from which they were able to observe "chiral" water1. Chirality is a property that favors the flow of materials that are indispensable to filtration. This work, conducted by CNRS researchers from the Institut Européen des Membranes (CNRS/ENSCM/Université de Montpellier) and the Laboratoire CNRS de Biochimie Théorique, in collaboration with US scientists, was published in Science Advances on March 23, 2018.
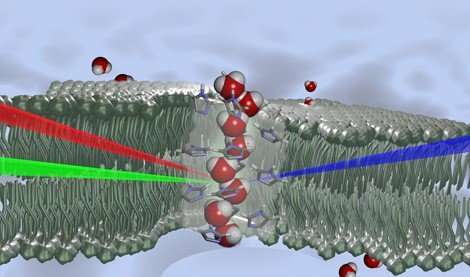
From a desire to develop breakthrough technologies for water filtration and purification, researchers have developed membranes with artificial channels inspired by the proteins that form the pores in biological membranes: aquaporins. Using an innovative spectroscopic technique, they have been able to observe that, in the very restricted space in these channels, water molecules organize in a very regular manner, in an oriented molecular wire structure : the water has become "chiral."
Identifying the chiral water in the artificial channels in these lipid membranes, under physiological conditions similar to natural pores, was a tour de force. This very regular arrangement of molecules had already been observed in solid structures of natural or artificial compounds, but is difficult to observe in solution, where the water molecules are very mobile.
This "wire" arrangement of water molecules is explained by the polarity of the water molecule conjugated with the asymmetry of the channels. Water, via hydrogen bonds, interacts with the walls of the artificial channels. In the resulting superstructures, the molecules forming the channels transmit their chiral character to the water threads, and give the water molecules a preferred direction. This led to the researchers' hypothesis: this collective orientation of water molecules probably plays an important role in the activation or the selection of transport through the membrane.
And indeed, laboratory experiments, supported by molecular dynamics calculations, confirmed that these chiral arrangements present greater transfer properties than their non-chiral equivalents, where water presents random molecular arrangement. In other words, the water's chirality causes greater mobility in nano-channels, boosting material transports, with a reduced exterior energy input.
This discovery opens a vast area of application for water filtration and purification. Currently, the researchers are developing reverse osmosis membranes, commonly used to desalinate sea water. They have already obtained promising results in terms of improved membrane permeability and selectivity, which are both indispensable criteria for filtration.
More information: Istvan Kocsis et al. Oriented chiral water wires in artificial transmembrane channels, Science Advances (2018). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aao5603
Journal information: Science Advances
Provided by CNRS