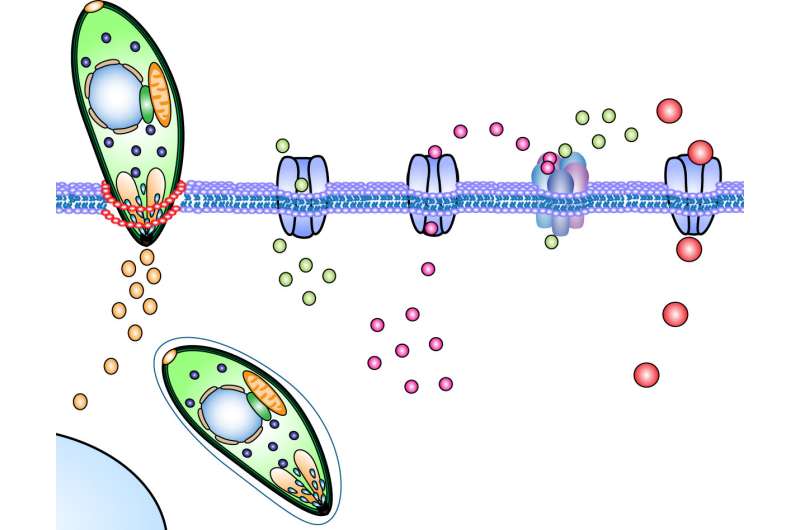
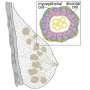
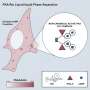
Image illustrates Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites invading across the cell membrane of a host cell. Upon invasion, a signaling cascade is activated via chloride channels, GABA channels and calcium signaling that mediates the migratory activation of the infected immune cell. Credit: S. Kanatani
The infection toxoplasmosis is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii and is widespread. It's estimated that 30 to 50 percent of the global human population are carriers. Cats are the parasites' main host, but the infection is also spread among other animals, including humans. A series of studies has previously shown that the parasite affects the brains of infected rats so that they lose fear of cats and even become attracted to cats' scent, making them an easy prey. The parasite spreads by ensuring that the rat is eaten by a cat. Toxoplasmosis is life-threatening to people with impaired immune systems and to unborn foetuses, but causes only mild symptoms in healthy individuals. However, there are studies showing that mental illnesses such as schizophrenia, depression and anxiety disorder are more common in people who are carriers of Toxoplasma gondii. There are also studies indicating that the parasite may affect aggressive or risky behaviour.
Researchers at Stockholm University have now been able to show how the parasite takes control and forces immune cells around the body to spread it, eventually reaching the brain. When we become infected with toxoplasma—for example, by eating insufficiently cooked meat or by contact with cat faeces—the parasite ends up in the stomach. It then passes through the intestinal wall and is met by immune cells that would normally kill it. Instead, immune cells become Trojan horses. By secreting the substance GABA, they can spread the infection into the body.
New research show that Toxoplasma gondii infects the human body by controlling our immune cells. They do so in a very smart way, says professor Antonio Barragan, Stockholm University. Credit: Stockholm University
"Is it a coincidence or evolution? It resembles how nerve cells speak to each other in our brains," said Antonio Barragan, professor at Stockholm University and one of the authors of the new study. The new research has shown that the small calcium molecule is the messenger in the communication. The researchers have found a new calcium receptor on immune cells, acting as a mailbox to receive the parasite's orders for the cell to move.
"The neat thing is that the signal can be inhibited by regular blood pressure medicine. When mice received the medicine, the spread of the parasite was inhibited. We do not want to say that blood pressure medicine can cure toxoplasmosis, but we have discovered a new signalling pathway in immune cells that is linked to their motility and that the parasite utilizes in a very smart way. This helps us understand how the parasite is spread and disease occurs. In the longer term, it may help us develop targeted treatments for infection," said Antonio Barragan.
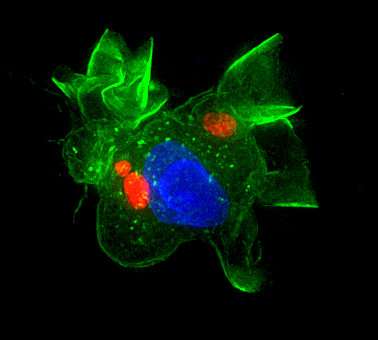
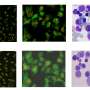
Image illustrate dendritic cell (green) infected by Toxoplasma gondii (red). Cell nuclei are stained in blue. Credit: Barragan lab
More information: Sachie Kanatani et al. Voltage-dependent calcium channel signaling mediates GABAA receptor-induced migratory activation of dendritic cells infected by Toxoplasma gondii, PLOS Pathogens (2017). DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006739
Journal information: PLoS Pathogens
Provided by Stockholm University