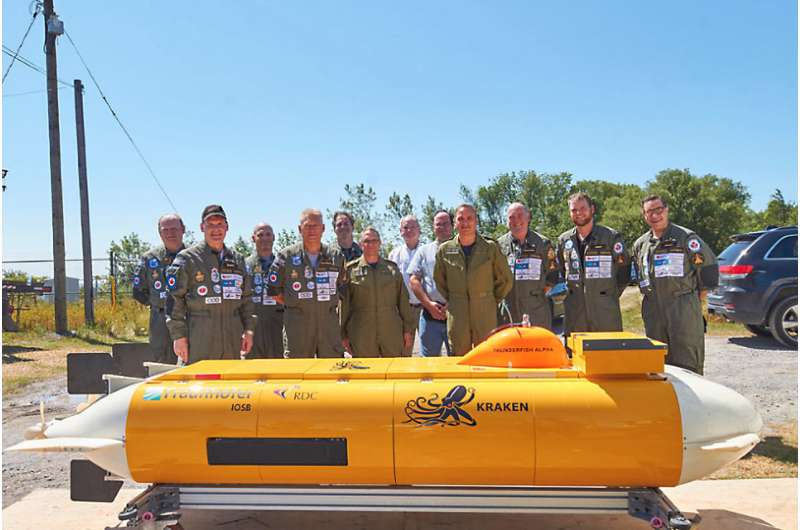
The “Raise the Arrow” team gathers for a photo behind the AUV. Credit: Fraunhofer IOSB-AST
DEDAVE is an innovative autonomous underwater vehicle developed by researchers at the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Now the deep-diving robot has had its first chance to prove itself in action as it helped hunt down historic test models of a Canadian interceptor aircraft in Lake Ontario. The mission has been a success, with two of the confirmed eight aircraft models already tracked down.
Designed for deepwater diving, autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) DEDAVE is capable of diving down to depths of 6000 meters to explore the seabed for sources of oil or minerals. The 3.5-meter-long lightweight construction was developed by researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute of Optronics, System Technologies and Image Exploitation IOSB in Ilmenau and Karlsruhe. DEDAVE is ready for large-scale industrial production, and has been licensed by the Canadian maritime technology company Kraken Robotics Inc., who have renamed it ThunderFish Alpha. Since the end of July, the AUV – which looks something like a space shuttle – has been helping the company hunt down the legendary delta-winged Avro Canada CF-105 interceptor in the waters of Lake Ontario (see information box). In September, ThunderFish Alpha got its first hit, locating the first and shortly after even a second model of the Arrow jet – a huge success, since people have been looking for wreckage of the supersonic aircraft for 50 years.
Sonar images generated in real time
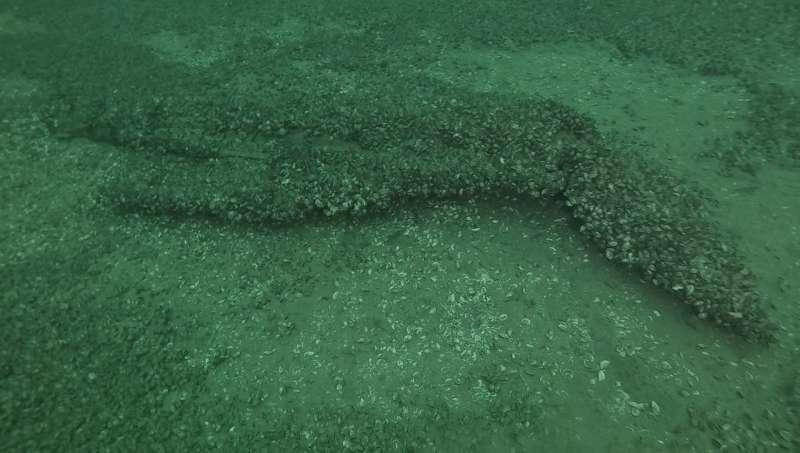
This sonar image from the ThunderFish AUV clearly shows fragments detected in Lake Ontario. Credit: Fraunhofer IOSB-AST
"We program in the route beforehand, and then ThunderFish Alpha autonomously scans the desired area of the lake bed using high-tech sonar equipment," says Helge Renkewitz, a researcher at Fraunhofer AST, a branch of Fraunhofer IOSB in Ilmenau, Germany. The scientist and his colleagues were on location for the search. Based on acoustic echoes, ThunderFish Alpha generates sonar images in real time, which can then be analyzed by the experts directly after the dive. Image data can be transferred wirelessly, and give precise indications of potential item locations.
Up to the end of September, the team was on the hunt. "During this period, ThunderFish detected 400 objects, 100 were already examined. Two of them proved to be the lost Arrow models that are scheduled for salvage before the end of the year," says Renkewitz. Meanwhile, the search has had to be put on hold because of the weather; it is to be continued from June to September 2018. All in all, ThunderFish has a surface area of 64 square kilometers to scan.
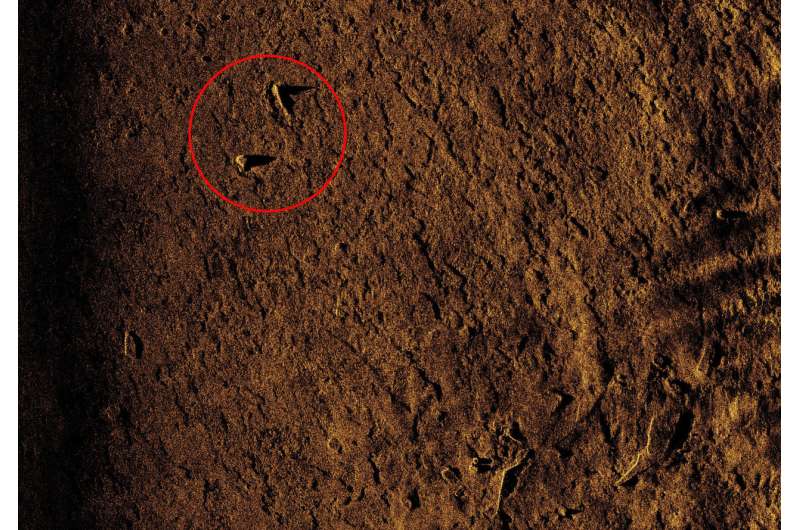
The first hit achieved with the help of Fraunhofer technology developed in Thuringia, Germany: A flight model of the CF-105 on the bed of Lake Ontario. Credit: Fraunhofer IOSB-AST
The AUV is powered by eight batteries, each weighing 15 kilograms apiece. A quick-release mechanism allows for these to be exchanged in a few minutes. A single battery charge is enough for 20 hours of exploration, and the software for the clever battery management system was developed in house
"We program in the route beforehand, and then ThunderFish Alpha autonomously scans the desired area of the lake bed using high-tech sonar equipment," says Helge Renkewitz, a researcher at Fraunhofer AST, a branch of Fraunhofer IOSB in Ilmenau, Germany. The scientist and his colleagues were on location for the search. Based on acoustic echoes, ThunderFish Alpha generates sonar images in real time, which can then be analyzed by the experts directly after the dive. Image data can be transferred wirelessly, and give precise indications of potential item locations.
Up to the end of September, the team was on the hunt. "During this period, ThunderFish detected 400 objects, 100 were already examined. Two of them proved to be the lost Arrow models that are scheduled for salvage before the end of the year," says Renkewitz. Meanwhile, the search has had to be put on hold because of the weather; it is to be continued from June to September 2018. All in all, ThunderFish has a surface area of 64 square kilometers to scan.
The first hit achieved with the help of Fraunhofer technology developed in Thuringia, Germany: A flight model of the CF-105 on the bed of Lake Ontario. Credit: Fraunhofer IOSB-AST
The AUV is powered by eight batteries, each weighing 15 kilograms apiece. A quick-release mechanism allows for these to be exchanged in a few minutes. A single battery charge is enough for 20 hours of exploration, and the software for the clever battery management system was developed in house at the Fraunhofer Institute for Silicon Technology ISIT in Itzehoe, Germany. The AUV also carries navigation sensors, two sonar modules, propulsion and steering units, communication modules, the software management system, data storage devices and a CAN-BUS system. This is a streamlined cable system that makes it possible to attach all the control units and electric motors. It offers certain advantages: for one, minimizing the amount of cables and connections minimizes malfunctions. What's more, attaching new modules, sensors or test devices to the standardized CAN-BUS is a quick and easy process. "The modularity of our AUV was one of the reasons Kraken chose DEDAVE," says Renkewitz.
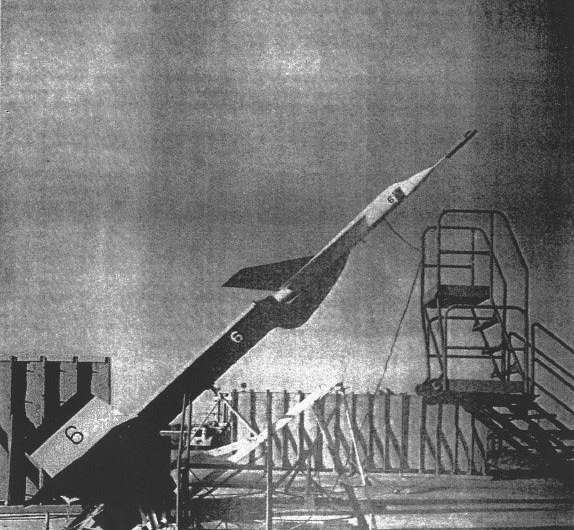
Old photo of a test model of the interceptor. Credit: Fraunhofer IOSB-AST
Provided by Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft