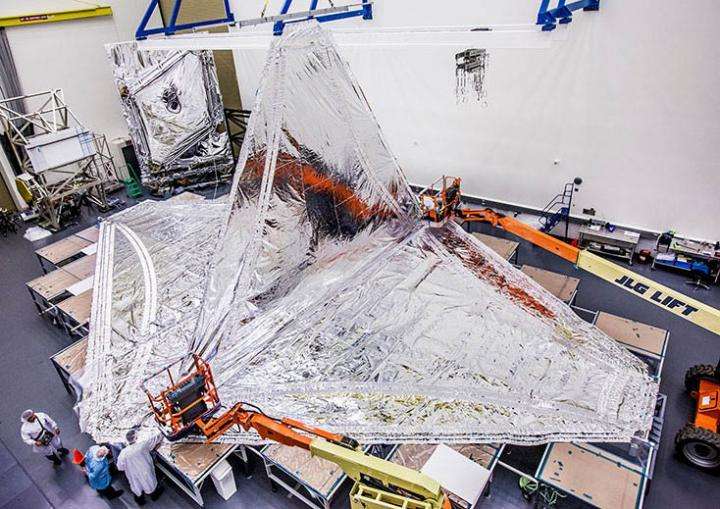
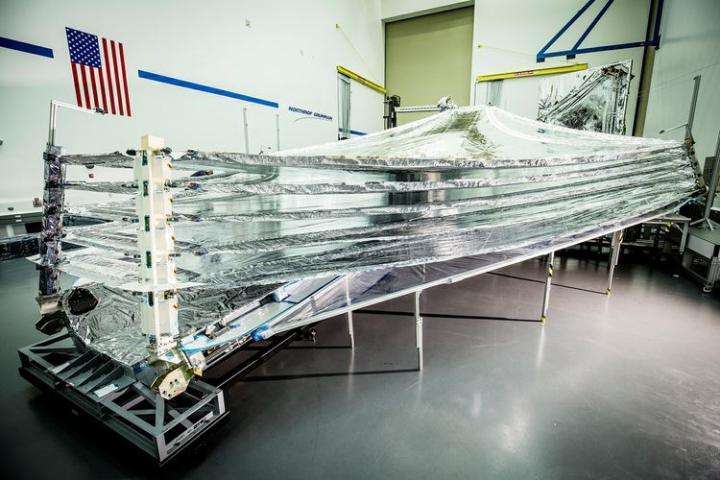
The first layer of the Webb telescope sunshield installed at Northrop Grumman's clean room in Redondo Beach, California. Credit: Northrop Grumman Corp.
The five sunshield layers responsible for protecting the optics and instruments of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope are now fully installed.
Northrop Grumman Corporation in Redondo Beach, California who designed the Webb telescope's optics and spacecraft bus for NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, integrated the final flight layers into the sunshield subsystem. The team is now folding and stowing the layers, in preparation for deployment tests in August.
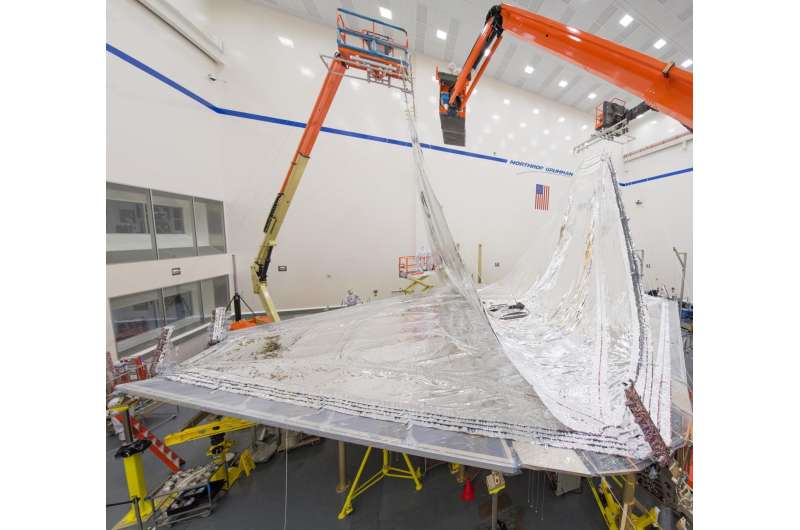
The sunshield layers work together to reduce the temperatures between the hot and cold sides of the observatory by approximately 570 degrees Fahrenheit. Each successive layer of the sunshield, made of kapton, is cooler than the one below. All layers were installed and tested in June and July 2017 at Northrop Grumman Corporation's Space Park facility in Redondo Beach.
"This is a huge milestone for the Webb telescope as we prepare for launch," said Jim Flynn, Webb sunshield manager, Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems. "The groundbreaking tennis court sized sunshield will shield the optics from heat and assist in providing the imaging of the formation of stars and galaxies more than 13.5 billion years ago."
All 5 layers of the Webb telescope sunshield installed at Northrop Grumman's clean room in Redondo Beach, California. The five sunshield membrane layers are each as thin as a human hair. Credit: : Northrop Grumman Corp.
"All five sunshield membranes have been installed and will be folded over the next few weeks," said Paul Geithner, deputy project manager - technical for the Webb telescope at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The Webb telescope's sunshield will prevent the background heat from the sun from interfering with the telescope's infrared sensors. The five sunshield membrane layers, designed and manufactured by the NeXolve Corporation in Huntsville, Alabama, are each as thin as a human hair. Because the sunshield is the size of a tennis court, it helps solidify the Webb telescope as the largest ever built for space. The sunshield, along with the rest of the spacecraft, will fold origami-style into an Ariane 5 rocket.
The Webb telescope is the world's next-generation space observatory and successor to the Hubble Space Telescope. The most powerful space telescope ever built, the Webb telescope will observe distant objects in the universe, provide images of the first galaxies formed and see unexplored planets around distant stars. The Webb Telescope is a joint project of NASA, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency.
The sunshield layers work together to reduce the temperatures between the hot and cold sides of the observatory by approximately 570 degrees Fahrenheit. Each successive layer of the sunshield, which is made of Kapton, is cooler than the one below. The sunshield is in the clean room at Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems in Redondo Beach, California. Credit: Northrop Grumman Corp.
Provided by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center