New proposal for a subspecies definition triggered by a new longhorn beetle subspecies
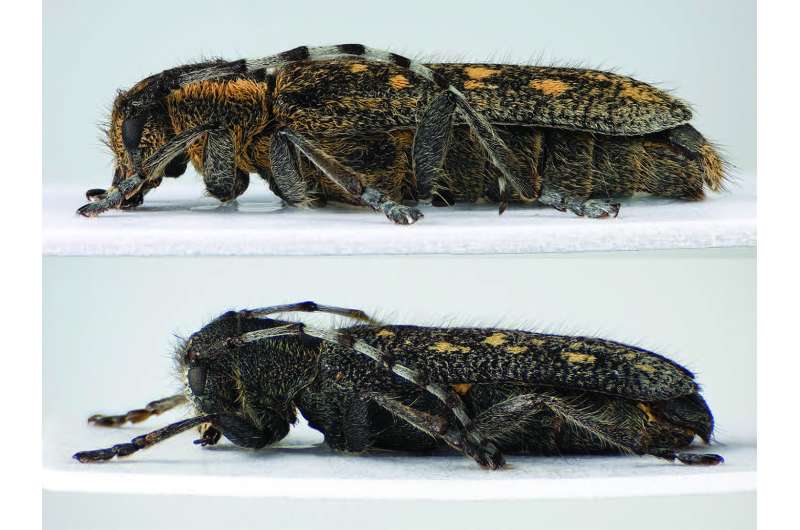

The discovery of a new subspecies of longhorn beetle from Scandinavia triggered a discussion on the vague organism classification rank 'subspecies'.
As a result, a newly proposed definition of subspecies has been published along with the description of the taxon in the open access journal ZooKeys by the research team of Henrik Wallin and Johannes Bergsten from the Swedish Museum of Natural History and Torstein Kvamme from the Norwegian Institute of Bioeconomy Research.
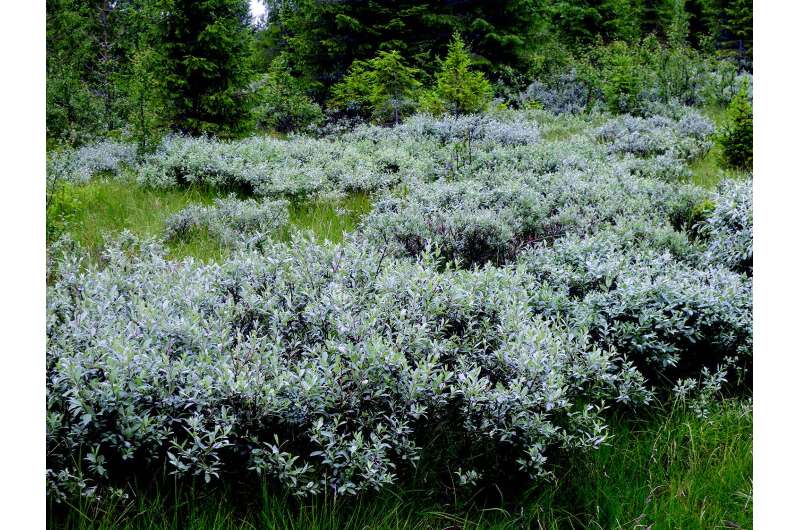
The northernmost populations of Saperda populnea display a number of divergent traits, including a shorter male antenna and reduced pubescens. In contrast with their most closely related subspecies (Saperda populnea populnea), whose favourite host plant, amongst others, is the European aspen, the new subspecies (Saperda populnea lapponica) specialised exclusively on downy willow (Salix lapponum).
According to the once no less disputed definition of species, regardless of their unique traits, populations cannot be considered as separate species until they are no longer able to produce fertile offspring according to the Biological Species concept, this being one of a number of proposed species concepts. A consensus is emerging around the unified species concept defining species as separately evolving (meta) population lineages.
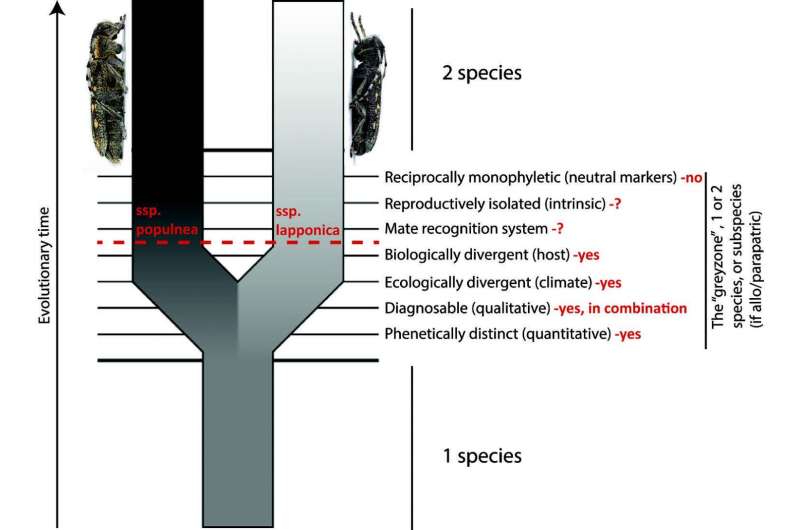
However, differentiating between subspecies nowadays is a significantly tougher task, since there is no stable definition of the rank yet. Through the years, there have been various explanations of what a subspecies is and what criteria it needs to meet in order to be classified as one.
Compared to previous definitions, the researchers decode it quite simply. To them, the only necessary attributes a population needs to possess before being deemed a subspecies are that they are a potentially incipient new species; diagnosed by at least one heritable trait; and either partially or completely isolated geographically.
Furthermore, they refute a number of factors, including reciprocal monophyly in neutral markers, the "75% rule", reproductive compatibility and the degree of gene flow.

The concept of subspecies has been so problematic that there have been even those scientists who have argued that taxonomy needs to discard it altogether.
However, the authors note that it is already formally recognised by the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN 1999), "albeit without giving any advice or criteria for its recognition."
"The concept is more than a mere academic debate as subspecies are recognized in various Red Lists and conservation programs, and hence the recognition as a subspecies or not can have legal and monetary consequences."
More information: Henrik Wallin et al, To be or not to be a subspecies: description of Saperda populnea lapponica ssp. n. (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) developing in downy willow (Salix lapponum L.), ZooKeys (2017). DOI: 10.3897/zookeys.691.12880
Journal information: ZooKeys
Provided by Pensoft Publishers